Elastic File System
Show slides
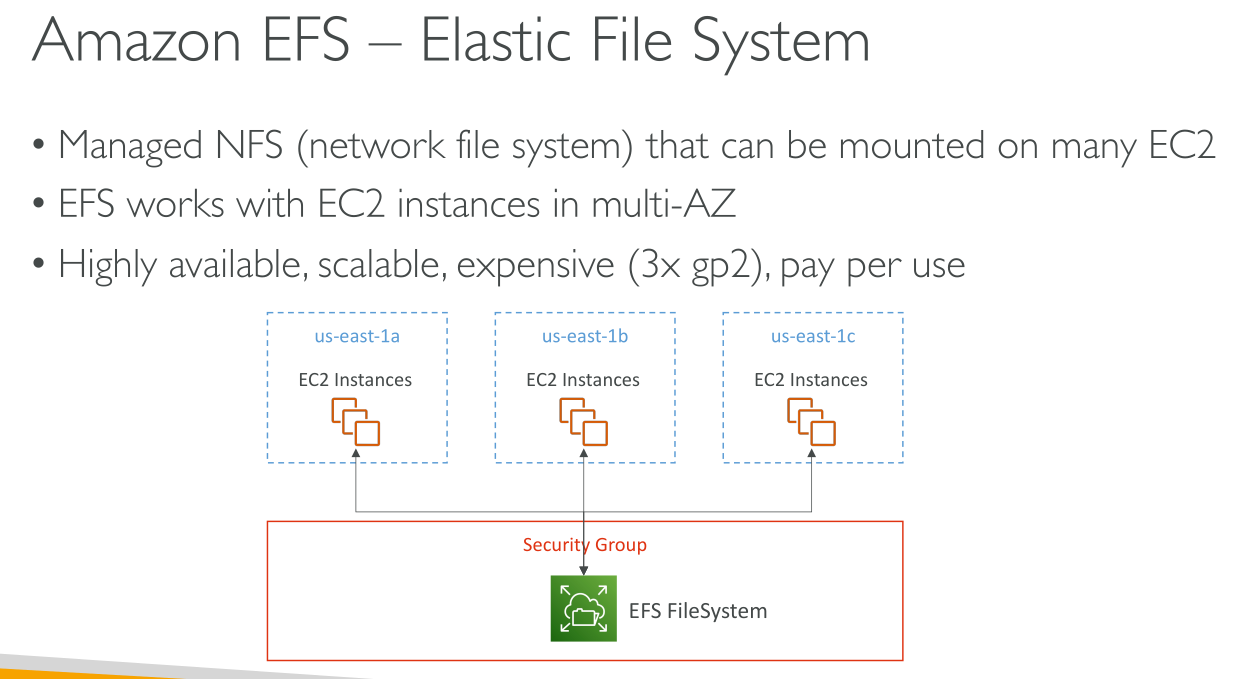

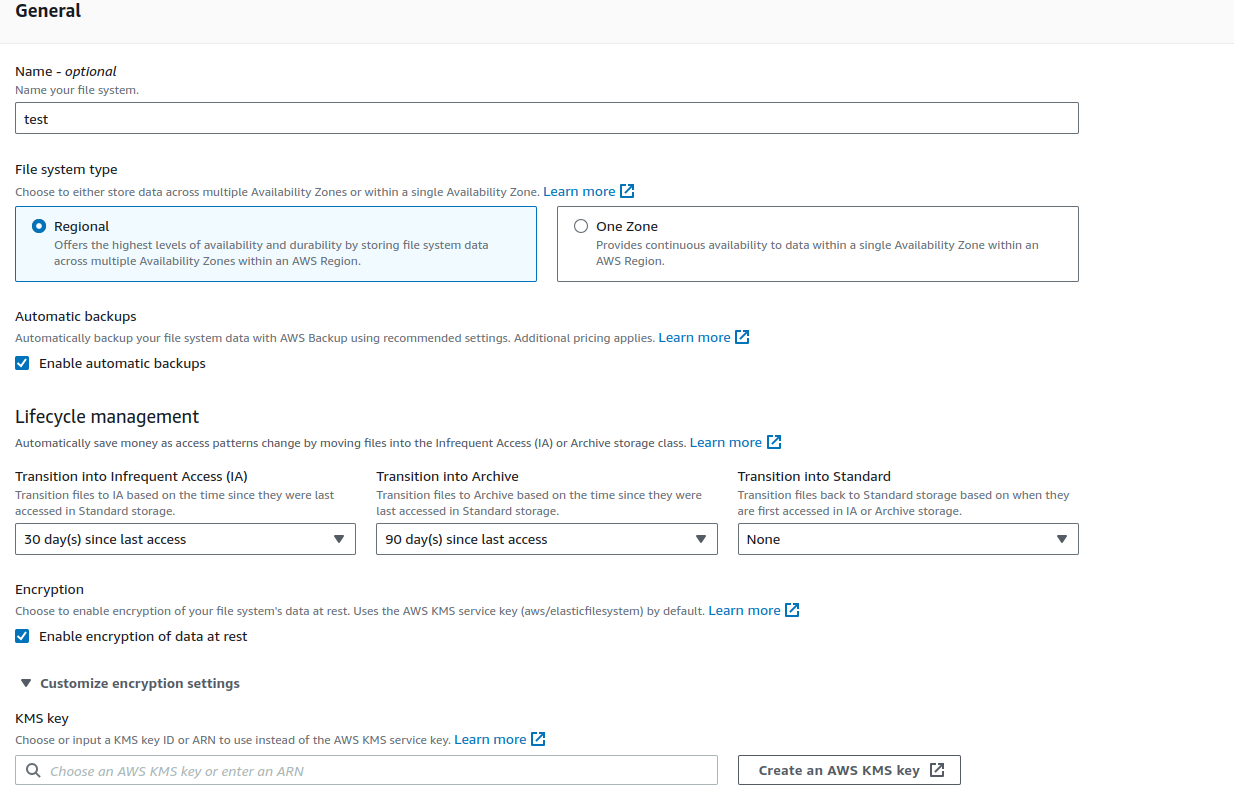
Amazon Elastic File System provides a simple, serverless, set-and-forget elastic file system.
Amazon EFS supports the Network File System version 4 (NFSv4.1 and NFSv4.0) protocol.
The service is designed to be highly scalable, highly available, and highly durable.
Amazon EFS supports:
-
authentication and authorization: NFS client access to EFS is controlled by both AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies and network security policies, such as security groups
-
encryption
-
encryption at rest: when creating an Amazon EFS file system. If you do, all of your data and metadata is encrypted.
-
encryption in transit: when you mount the file system.
-
Only Linux is officially supported.
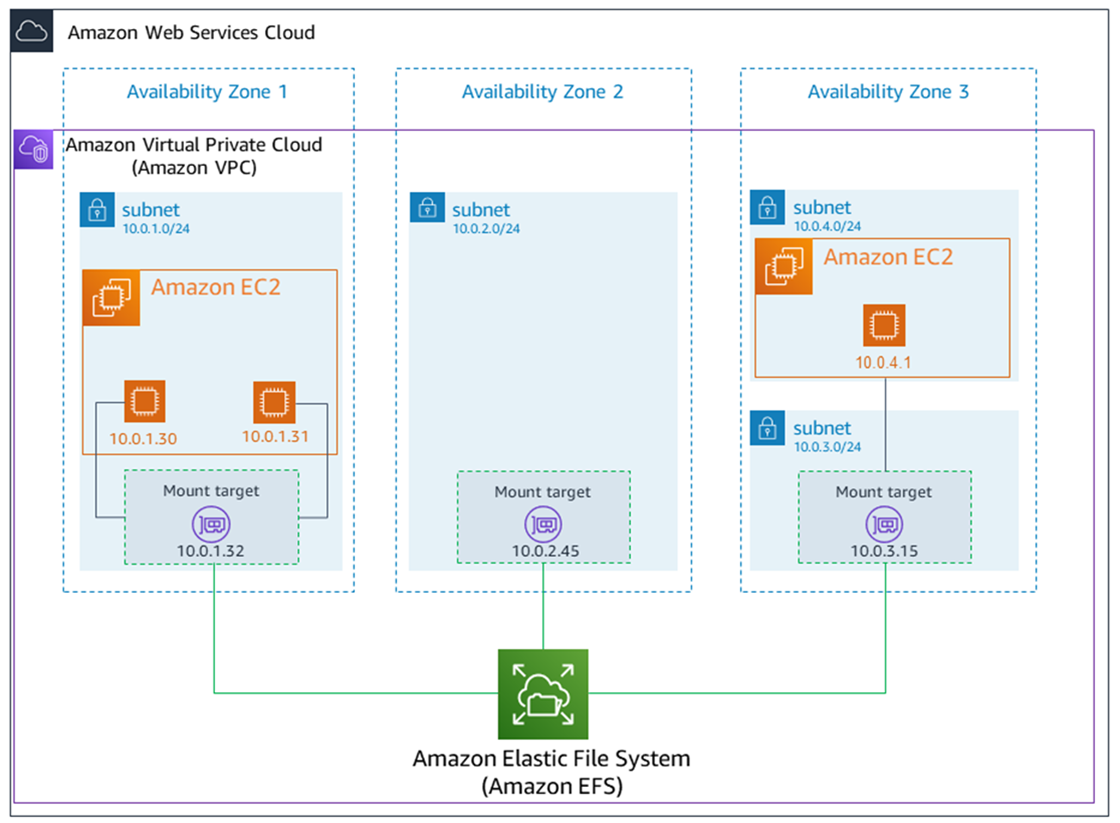
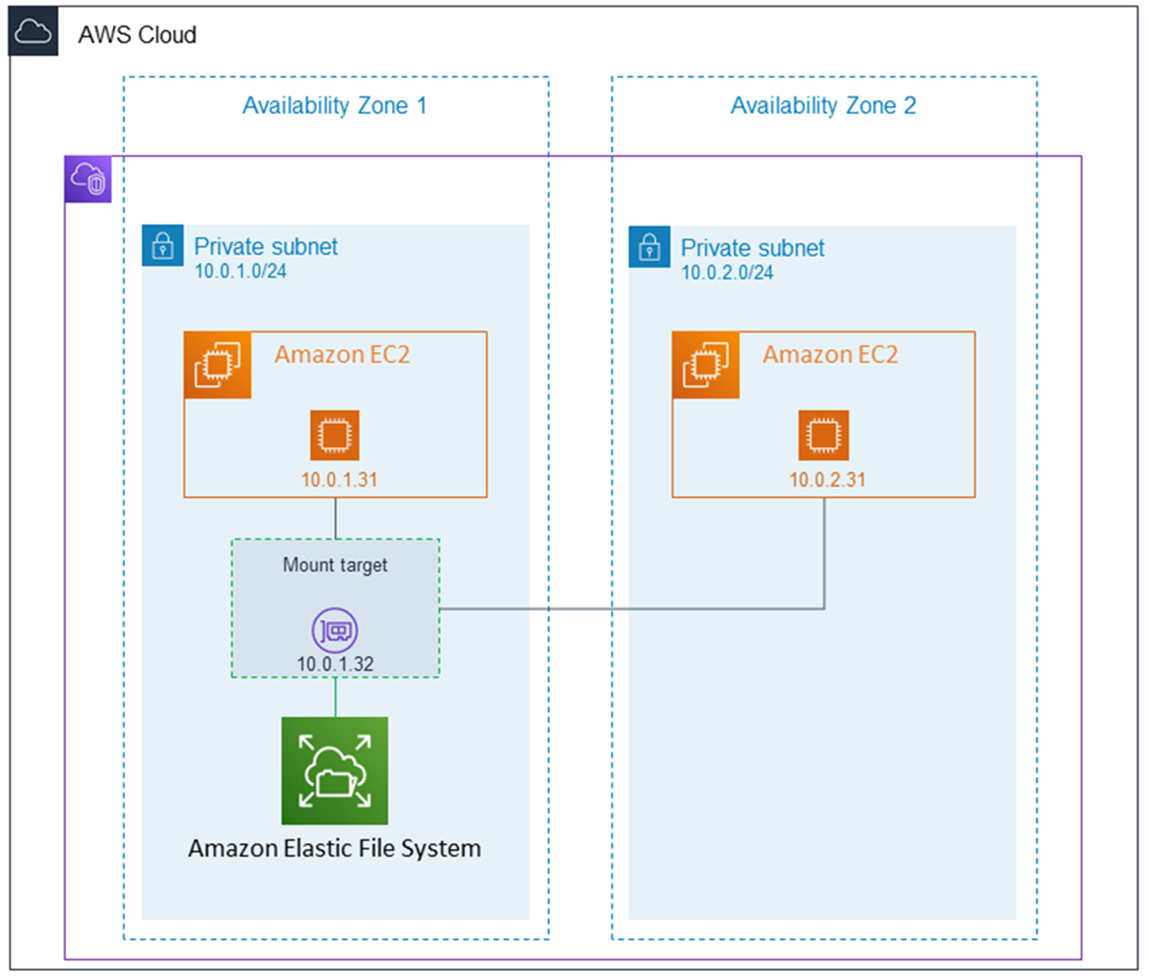
You can access your Amazon EFS file system concurrently from multiple NFS clients. Amazon EC2 and other AWS compute instances running in multiple Availability Zones within the same AWS Region can access the file system, so that many users can access and share a common data source.
A mount target provides an IP address for an NFSv4 endpoint at which you can mount an Amazon EFS file system. You mount your file system using its Domain Name Service (DNS) name, which resolves to the IP address of the EFS mount target in the same Availability Zone as your EC2 instance. You can create one mount target in each Availability Zone in an AWS Region. If there are multiple subnets in an Availability Zone in your VPC, you create a mount target in one of the subnets. Then all EC2 instances in that Availability Zone share that mount target.
The security groups that you associate with a mount target must allow inbound access for the TCP protocol on the NFS port from all EC2 instances on which you want to mount the file system. Each EC2 instance that mounts the file system must have a security group that allows outbound access to the mount target on the NFS port.
Since mount targets are available in a subnet they can be reached as subnet endpoints: this includes Hybrid Connectivity services (like VPC or Direct Connect that allow on-prem to connect to cloud), VPC Peering and shared VPCs.
Regional EFS:
One Zone EFS:
NFS client applications can use NFS version 4 file locking (512 locks max per file).
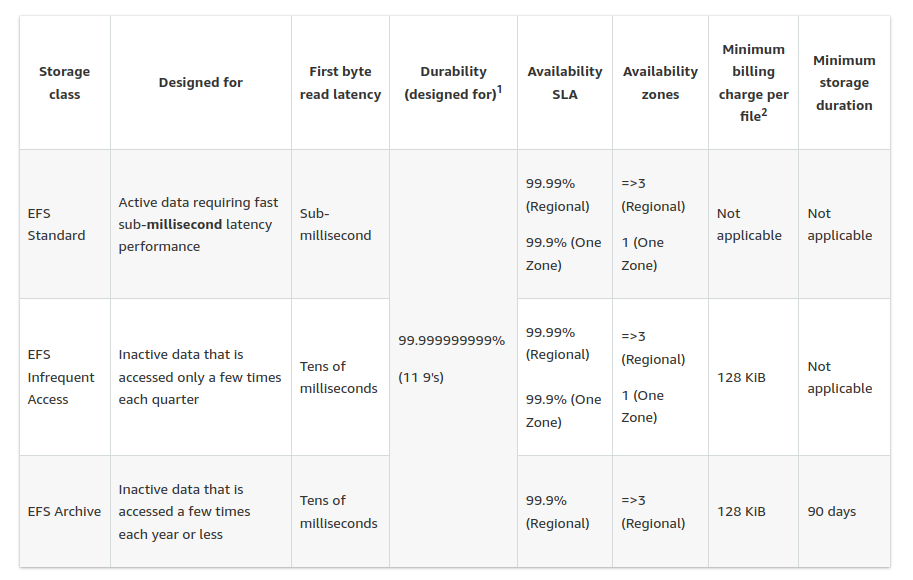
Storage classes
-
Standard: SSD storage. Sub-millisecond latency.
-
Infrequent Access (IA): ideal for accessing data only a few times each quarter.
-
Archive: ideal for accessing data only a few times each year.
First byte latency when reading from either of the infrequently accessed storage classes is higher than that for the Standard storage class.
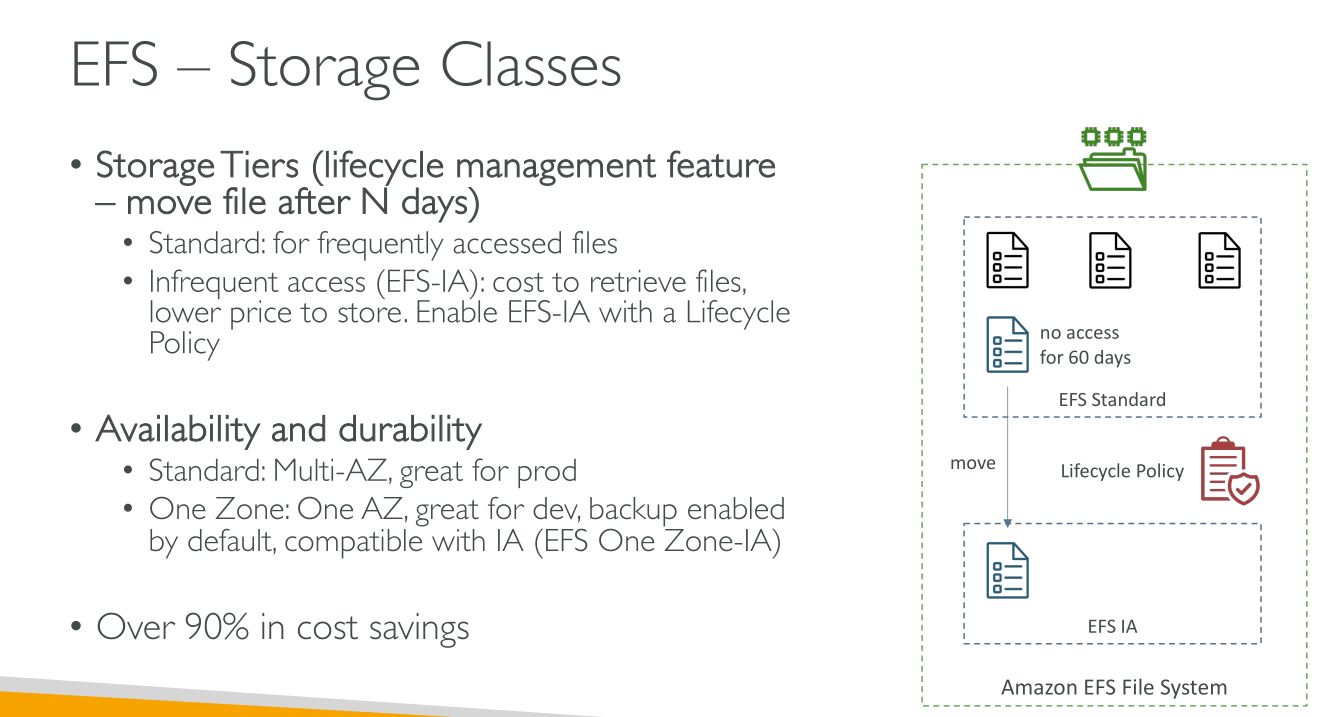
Lifecycle Policies
Using lifecycle management, you can optimize storage costs by automatically tiering data between storage classes based on your workload’s access patterns. You can move files from the IA or Archive storage classes to the Standard storage class by setting the Transition into Standard lifecycle policy on your file system. This setting transitions files from IA or Archive back to Standard upon access.
Default Lifecycle policy:
-
Transition to IA after 30 days since last access.
-
Transition to Archive after 90 days since last access.
-
Transition to Standard is set to None.
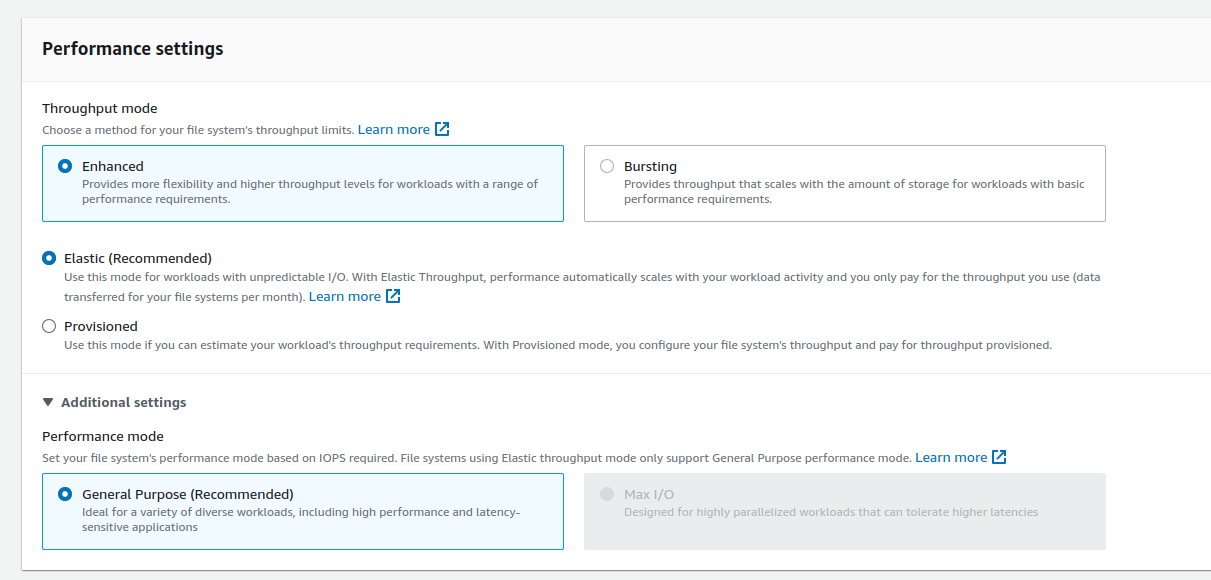
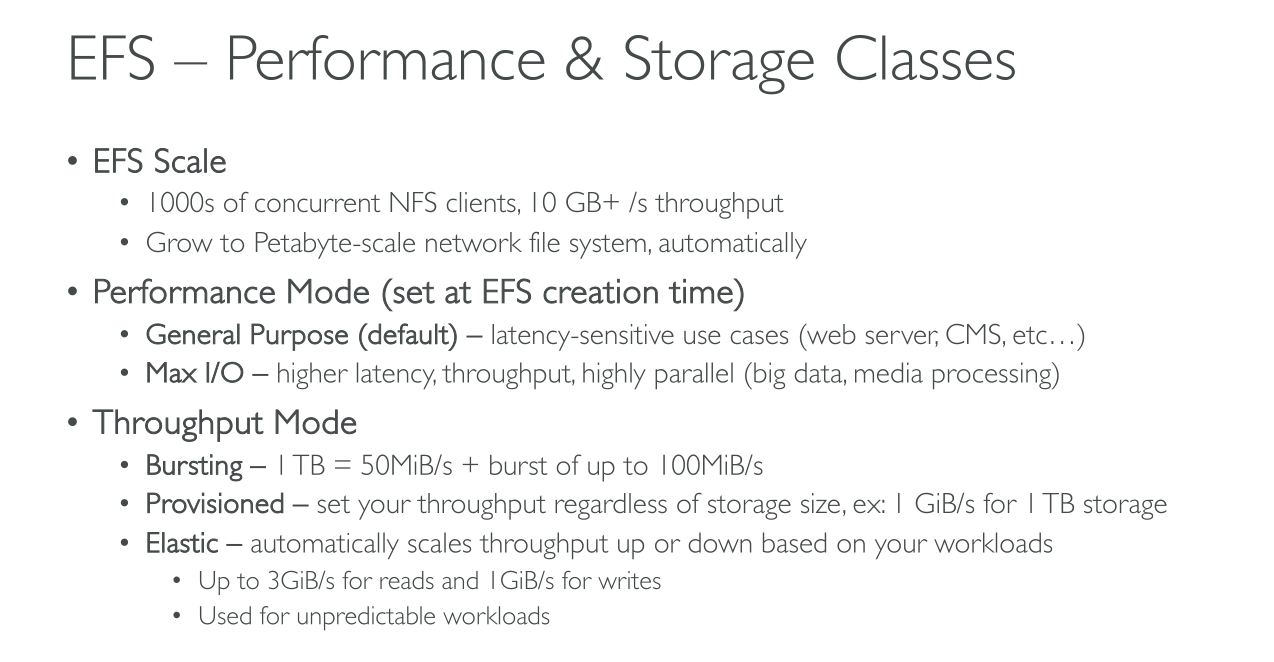
Throughput Modes
-
Enhanced:
-
Elastic (Recommended): performance automatically scales up or down to meet the needs of your workload activity. For unpredictable workloads.
-
Provisioned: You specify a level of throughput that the file system can drive independent of the file system’s size or burst credit balance. For high performance workloads or when you have >= 5% average-to-peak throughput needs.
-
-
Bursting: Throughput scales with the amount of storage in your file system and supports bursting to higher levels for up to 12 hours per day. It uses GP2 so performance scales with the size of the storage.
You can change the throughput mode and the provisioned throughput amount after the file system is available. However, any time that you change the file system to Provisioned throughput or increase the provisioned throughput amount, you must wait at least 24 hours before you can change the throughput mode again or decrease the provisioned amount.
Performance modes
-
General purpose: has the lowest per-operation latency and is the default performance mode for file systems. One Zone file systems always use the General Purpose performance mode. TOP PERFORMANCE. Used for
-
Home directories
-
Web Servers
-
CMSs
-
General file serving on linux
-
-
Max I/O: previous generation performance type that is designed for highly parallelized workloads that can tolerate higher latencies than the General Purpose mode. It us unsupported for One Zone file systems and Elastic throughput mode. Used for
-
Big Data
-
Media processing
-
Scientific analysis
-