Api Gateway
Architecturally it sits between applications which utilize APIs and the integrations which are the backend services which provide the functionality of that API.
API Gateway is a public facing, managed, highly available and scalable service by default
It provides HTTP, REST and Websocket as protocols.
API Gateway can integrate with CloudWatch to store logging and metric based data for request and response side operations.
Architecture
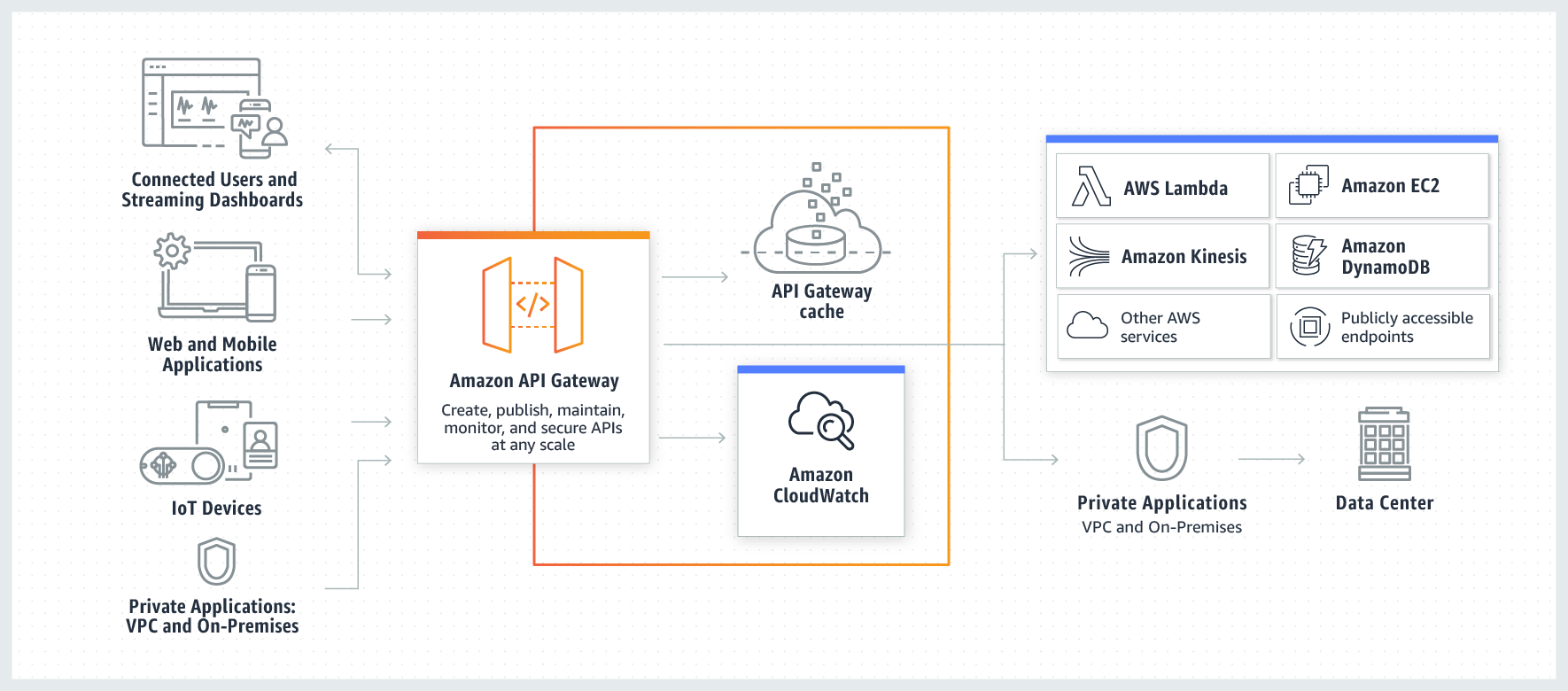
The API Gateway’s job is to act as an intermediary between clients and integrations, the backend services which provide the functionality to API Gateway.
There are three phases in most API Gateway interactions:
-
The request phase: the client makes a request to the API Gateway
-
The integration phase: the API Gateway calls to the service provided by the configured integrations with some payload.
-
The response phase where the response is provided back to the client.
Features
-
Authorization
-
Request Throttling,
429 HTTP Status Code -
Caching
-
CORS support
-
Request and Response transformation
-
OpenAPI Spec format for importing and exporting
-
Direct integration with AWS services like DynamoDB, Lambda, Step Functions, SNS and so on
-
Integration with on-prem services
-
Workload migration (from on-prem) or rearchitecturing from monolithic architectures to others
Authentication
Authentication can be:
-
None
-
Cognito based: the client authenticates with Cognito and receives a Cognito token in return if authentication succeeds. The token is passed to API Gateway that validates it.
-
Lambda based authentication using a Lambda Authorizer: this is a flexible mechanism in which the code inside the Lambda Function takes care of all, it allows custom authentication mechanism (user store, custom ID provider and so on). The Lambda Function returns an IAM Principal and an IAM Policy in case of successful authentication. Depending on the result returned by the Lambda Function the API Gateway will accept the request or not.
-
Authorization Header: credentials can be sent in a header.
Endpoint Types
Stages
An API stage is a logical reference to a lifecycle state of your API (for example, dev, prod, beta, or v2).
Each stage has its own unique endpoint URL as well as its own settings and can be deployed onto individually.
You might have v1 of the API configuration deployed into production, which uses version 1 of a Lambda function as a backing integration.
You might also have version two, which is currently under development deployed into the dev stage, which could use a separate backing Lambda function containing the new code.
Canary Deployments
Stages allow for Canary Deployments: any new deployments you make to the stage are actually deployed on a sub part of that stage, the canary part of that stage, and not the stage itself. Eventually the canary can be promoted to be the base stage and the process repeated. You can adjust the distribution of traffic between a production stage and its canary until you’re completely happy and then promote the canary to be the full base stage and this process of development production cycles can then continue.
Version two can be deployed onto production and this will be deployed into the canary because canary is enabled on the production stage.
Caching
Caching can be defined at the Stage level and allows to cache content from 500 MB to 237GB. Cached content is encrypted.
The default TTL for cached content is 300. It can be set from 0 (disabled) to 3600s.
Of course caching means fewer requests to the backend layer.
HTTP Error Codes
Client:
-
400: Bad Request (generic)
-
401: Unauthorized
-
403: Forbidden
-
405: Method not allowed
-
415: Unsupported Media Type
-
429: Too Many Requests (the API Gateway or something else is throttling traffic)
Server:
-
502: Bad Gateway
-
503: Service Unavailable.
-
504: Gateway Timeout. There might be a problem with the backend integration. The default timeout for integrations is 29s so if a Lambda takes 5 minutes to return a result the gateway times out.