Placement groups
Show slides
Placement strategies
Note: The instance TYPE must support the placement strategy you choose. For example t3.large does not support Cluster.
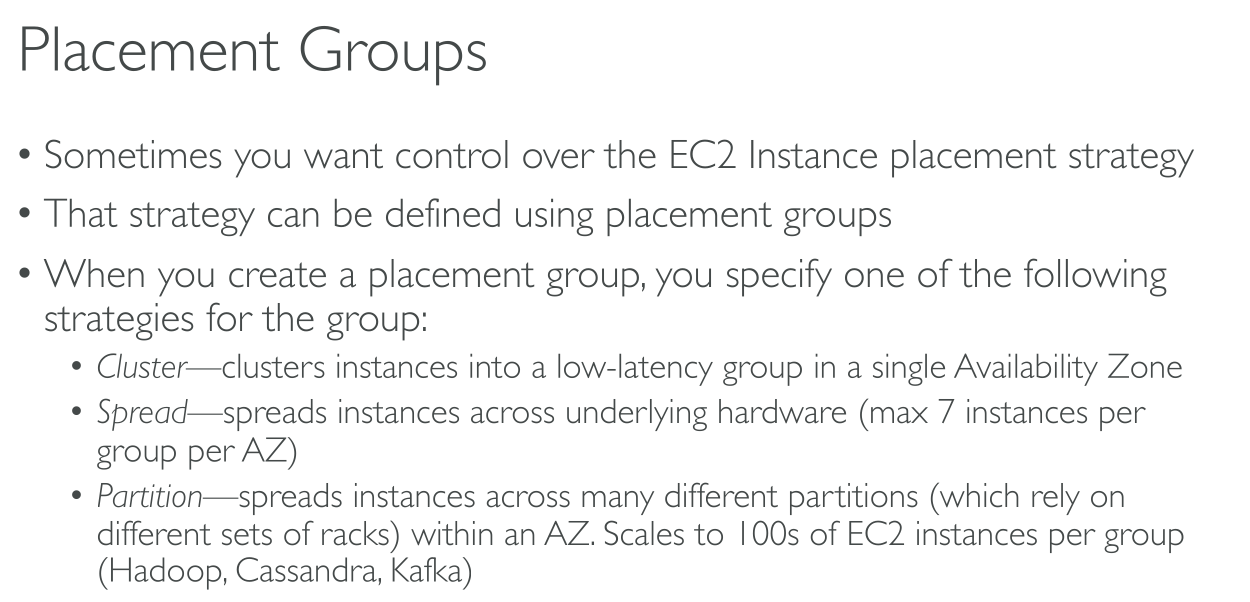
Cluster
Packs instances close together inside an Availability Zone. This strategy enables workloads to achieve the low-latency network performance necessary for tightly-coupled node-to-node communication that is typical of high-performance computing (HPC) applications (10Gbps on single stream). Instances are scheduled on the same rack and often on the same host. It is required if you want to max speed, but you also have to enable Enhanced Networking. It’s only available on some instance types.
You should use the same instance type so that there’s no bottleneck, but you also should launch all the instances at the same time because adding instances later doesn’t guarantee there will be space for others.
An AZ or datacenter failure means breaking the service.
They’re limited to a single AZ but you can’t specify an AZ.
VPC peering can be used but really impacts performance.
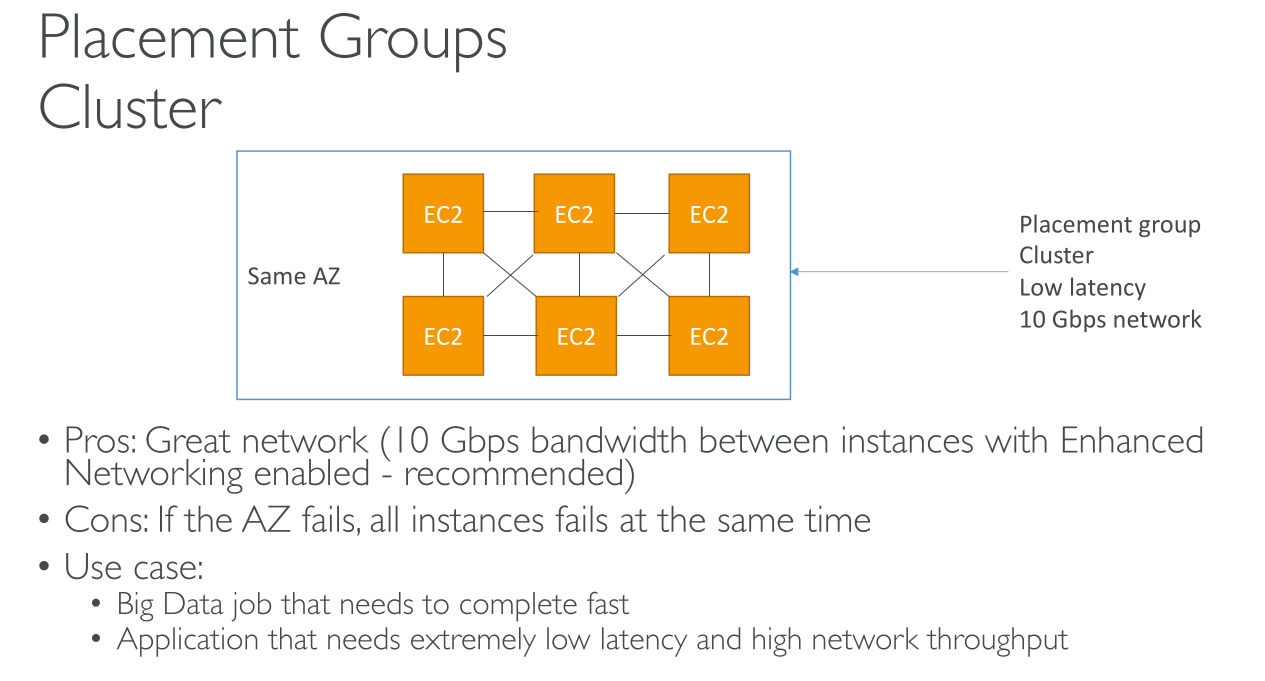
Spread
Strictly places a small group of instances across distinct underlying hardware to reduce correlated failures. They’re optimal to segregate the blast radius.
It spans across AZs and places instances so that each has isolated network and power supply.
There’s a limit of 7 instances per Placement Group per AZ.
You cannot use Dedicated Instances or Dedicated Hosts.
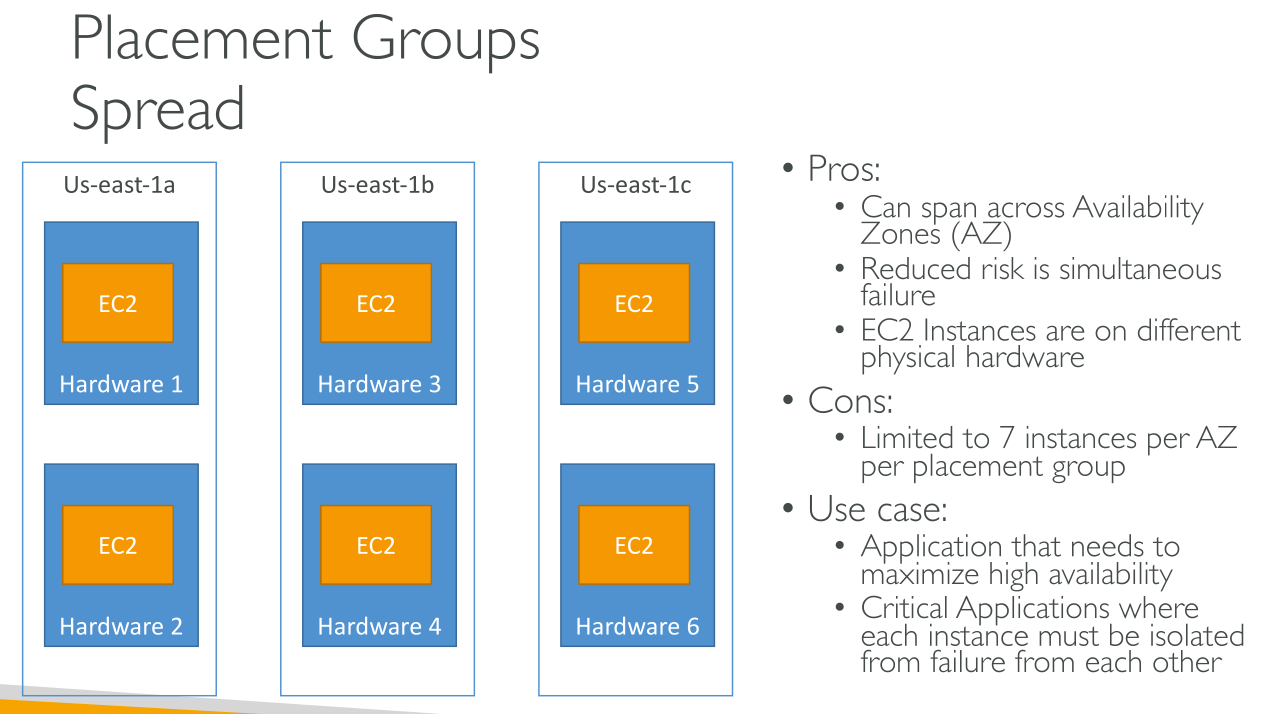
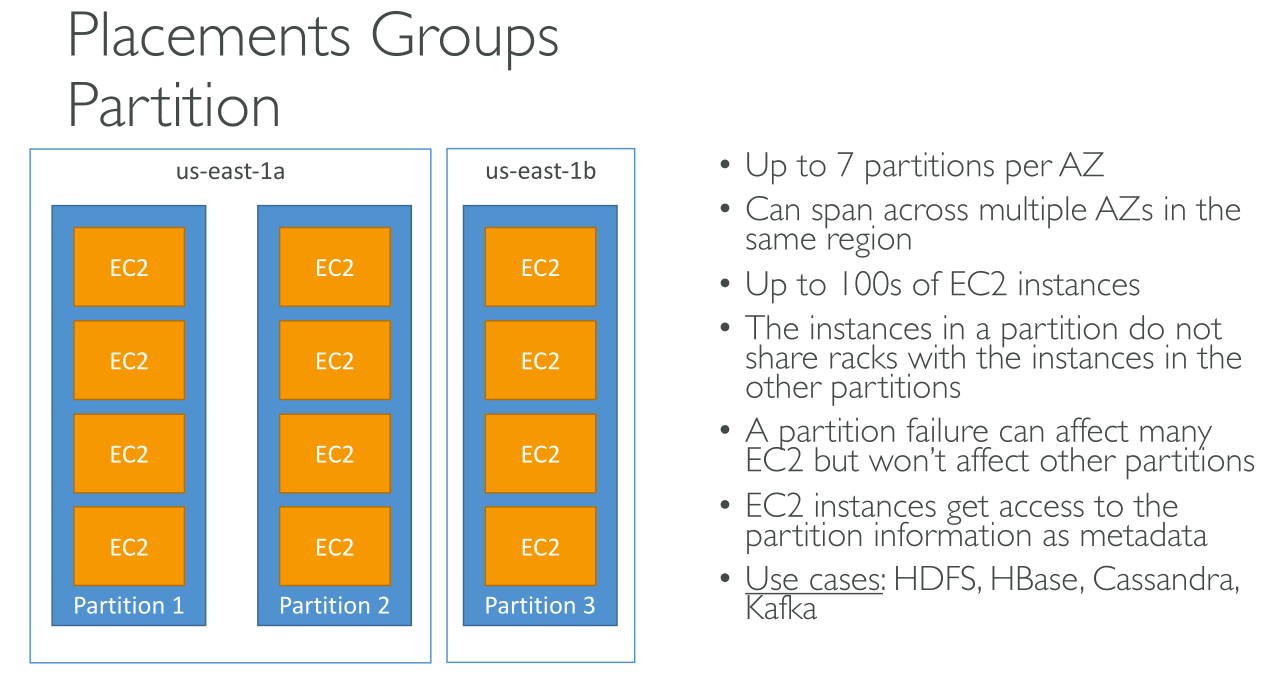
Partition
Spreads your instances across logical partitions such that groups of instances in one partition do not share the underlying hardware with groups of instances in different partitions. This strategy is typically used by large distributed and replicated workloads, such as Hadoop, Cassandra, and Kafka.
Each partition has a separate network access and power supply.
You can use this if you have more than 7 instances but still want to spread them in the region.
You can have up to 7 partitions per AZ and up to 100 instances in the group. You decide in which partition to create new instances.
Designed for huge scale parallel systems and system with built-in replication and that are topology-aware.
With Spread you have the maximum management and your application doesn’t need to be aware of its components' placement. With Partition you can reach the same if your application is topology-aware. ⇒ HDFS, HBase, Cassandra.
Limitations
-
maximum of 500 placement groups per account in each Region.
-
The name that you specify for a placement group must be unique within your AWS account for the Region.
-
You can’t merge placement groups
-
You can’t launch Dedicated Hosts in placement groups.
-
You can’t launch a Spot Instance that is configured to stop or hibernate on interruption in a placement group