Purchasing options
Show slides
On-Demand Instances
Show slides

You pay for compute capacity by the second with no long-term commitments. You have full control over the instance’s lifecycle—you decide when to launch, stop, hibernate, start, reboot, or terminate it.
There is no long-term commitment required when you purchase On-Demand Instances. You pay only for the seconds that your On-Demand Instances are in the running state, with a 60-second minimum.
-
Linux or Windows - billing per second, after the first minute
-
All other operating systems - billing per hour
Reserved instances
Show slides

Reserved Instances are not physical instances, but rather a billing discount applied to the use of On-Demand Instances in your account. These On-Demand instances must match certain attributes, such as instance type and Region, in order to benefit from the billing discount.
|
AWS recommends Saving Plans over Reserved Instances: |
Attributes for eligibility (!)
-
Platform (Linux/Windows)
-
Instance Type
-
Availability Zone
-
Tenancy (Dedicated/Shared)
Payment options
-
All Upfront: Full payment is made at the start of the term, with no other costs or additional hourly charges incurred for the remainder of the term, regardless of hours used.
-
Partial Upfront: A portion of the cost must be paid upfront and the remaining hours in the term are billed at a discounted hourly rate, regardless of whether the Reserved Instance is being used.
-
No Upfront: You are billed a discounted hourly rate for every hour within the term, regardless of whether the Reserved Instance is being used. No upfront payment is required.
|
No Upfront Reserved Instances are based on a contractual obligation to pay monthly for the entire term of the reservation. For this reason, a successful billing history is required before you can purchase No Upfront Reserved Instances. |
Offering class
-
Standard: These provide the most significant discount, but can only be modified. Standard Reserved Instances can’t be exchanged.
-
Convertible: These provide a lower discount than Standard Reserved Instances, but can be exchanged for another Convertible Reserved Instance with different instance attributes. Convertible Reserved Instances can also be modified.
Scope
-
Zonal: A zonal Reserved Instance reserves capacity in the specified Availability Zone. No Availability Zone flexibility. No instance size flexibility — the Reserved Instance discount applies to instance usage for the specified instance type and size only. The attributes (tenancy, platform, Availability Zone, instance type, and instance size) of the running instances must match that of the Reserved Instances.
-
Regional: A regional Reserved Instance does not reserve capacity. The Reserved Instance discount applies to instance usage in any Availability Zone in the specified Region. The Reserved Instance discount applies to instance usage within the instance family, regardless of size with a partial effect for instances larger than the configuration you reserved (Only supported on Amazon Linux/Unix Reserved Instances with default tenancy).
Instance size flexibility determined by normalization factor.
Modifying reserved instances
You can modify all or a subset of your Reserved Instances. You can separate your original Reserved Instances into two or more new Reserved Instances. For example, if you have a reservation for 10 instances in us-east-1a and decide to move 5 instances to us-east-1b, the modification request results in two new reservations: one for 5 instances in us-east-1a and the other for 5 instances in us-east-1b.
You can also merge two or more Reserved Instances into a single Reserved Instance. For example, if you have four t2.small Reserved Instances of one instance each, you can merge them to create one t2.large Reserved Instance.
Saving plans
Show slides
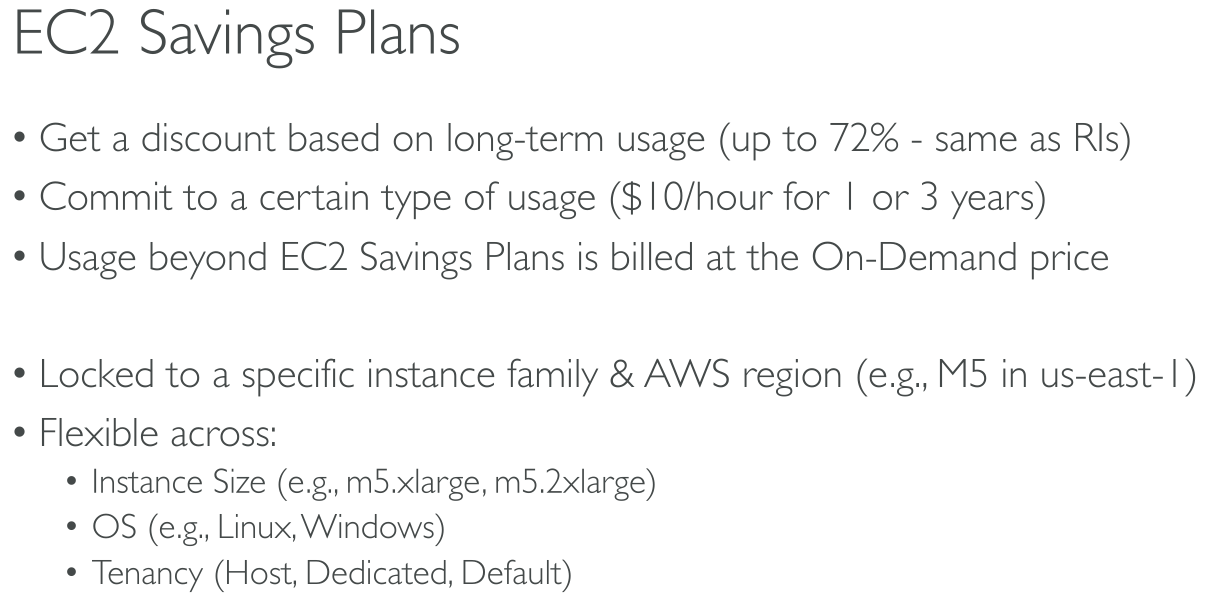
A flexible pricing model offering lower prices compared to On-Demand pricing, in exchange for a specific usage commitment (measured in $/hour) for a one- or three-year period
Compute saving plans
These plans automatically apply to EC2 instance usage regardless of instance family, size, AZ, region, OS or tenancy, and also apply to Fargate and Lambda usage.
You can change from C4 to M5 instances, shift a workload from EU (Ireland) to EU (London), or move a workload from EC2 to Fargate or Lambda at any time and automatically continue to pay the Savings Plans price.
EC2 Instance Savings Plans
provide the lowest prices, offering savings up to 72% in exchange for commitment to usage of individual instance families in a region (e.g. M5 usage in N. Virginia).
EC2 Instance Savings Plans give you the flexibility to change your usage between instances within a family in that region
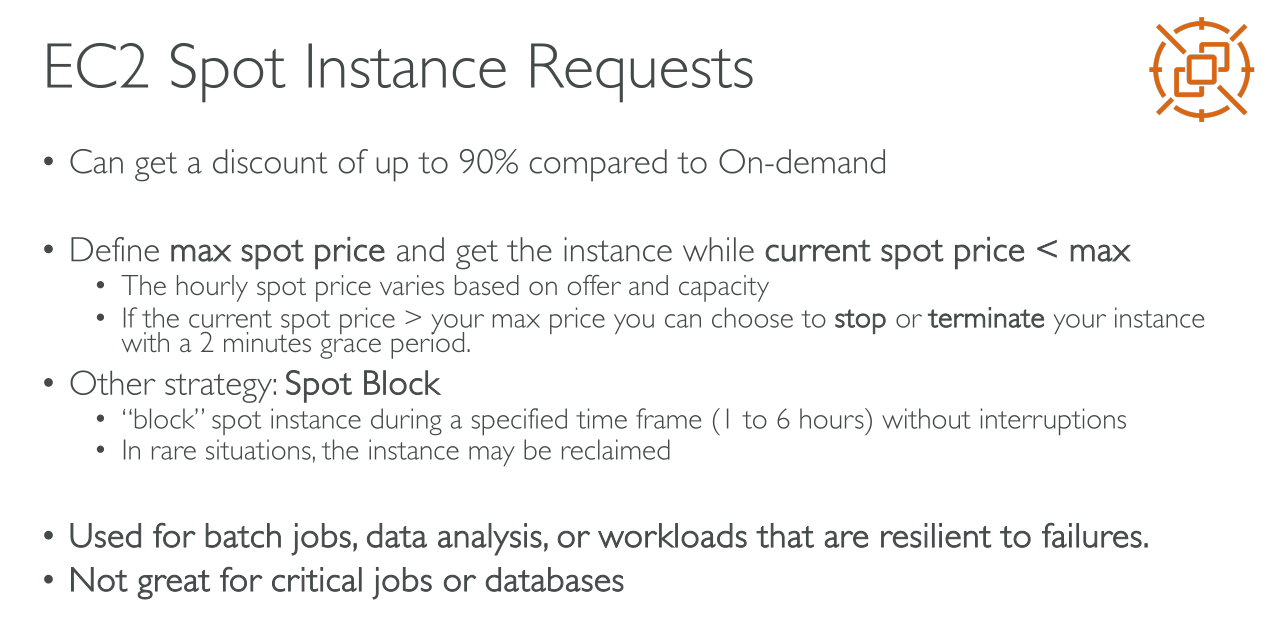
Spot Instances
Show slides

Concepts
-
Spot capacity pool – A set of unused EC2 instances with the same instance type (for example, m5.large) and Availability Zone.
-
Spot price – The current price of a Spot Instance per hour.
-
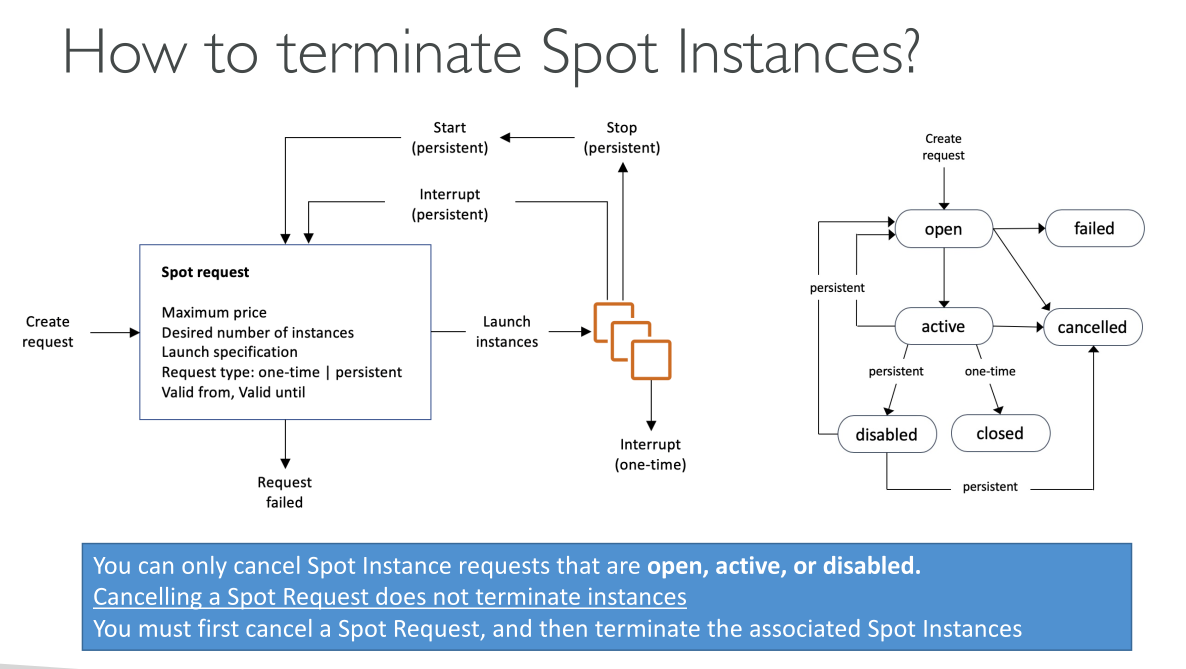
Spot Instance request – Requests a Spot Instance. When capacity is available, Amazon EC2 fulfills your request. A Spot Instance request is either one-time or persistent. Amazon EC2 automatically resubmits a persistent Spot Instance request after the Spot Instance associated with the request is interrupted.
-
EC2 instance rebalance recommendation – Amazon EC2 emits an instance rebalance recommendation signal to notify you that a Spot Instance is at an elevated risk of interruption. This signal provides an opportunity to proactively rebalance your workloads across existing or new Spot Instances without having to wait for the two-minute Spot Instance interruption notice.
-
Spot Instance interruption – Amazon EC2 terminates, stops, or hibernates your Spot Instance when Amazon EC2 needs the capacity back. Amazon EC2 provides a Spot Instance interruption notice, which gives the instance a two-minute warning before it is interrupted.
With spot instances AWS sets a price for unused capacity (Spot price) depending on AZ, machine type and overall available capacity. You define a Max price you’re willing to pay (must be higher than Spot price) for instances, and as long as your price is greater than or equal to the Spot price you keep paying the spot price. If the Spot price raises above your thereshold your instances are terminated (or whatever options you set in the request; One-time requests only allow for termination).
Request types
-
A one-time Spot Instance request remains active until Amazon EC2 launches the Spot Instance, the request expires, or you cancel the request. If capacity is not available, your Spot Instance is terminated and the Spot Instance request is closed.
-
A persistent Spot Instance request remains active until it expires or you cancel it, even if the request is fulfilled. If capacity is not available, your Spot Instance is interrupted. After your instance is interrupted, when capacity becomes available again, the Spot Instance is started if stopped or resumed if hibernated. You can stop a Spot Instance and start it again if capacity is available. If the Spot Instance is terminated (irrespective of whether the Spot Instance is in a stopped or running state), the Spot Instance request is opened again and Amazon EC2 launches a new Spot Instance.
Best practices
-
Prepare individual instances for interruptions
-
Be flexible about instance types and Availability Zones
-
Use EC2 Auto Scaling groups or EC2 Fleet to manage your aggregate capacity
-
Use the price and capacity optimized allocation strategy: because this strategy automatically provisions instances from the most-available Spot capacity pools that also have the lowest possible price. You can also take advantage of the price-capacity-optimized allocation strategy in EC2 Fleet
-
Use proactive capacity rebalancing
-
Monitor rebalance recommendation signals: The rebalance recommendation signal is made available as an event that is sent to Amazon EventBridge (formerly known as Amazon CloudWatch Events) and as instance metadata on the Spot Instance
Dedicated Hosts
Show slides
An Amazon EC2 Dedicated Host is a physical server that is fully dedicated for your use.
Dedicated Hosts provide visibility and control over instance placement and they support host affinity. This means that you can launch and run instances on specific hosts, and you can ensure that instances run only on specific hosts. For more information, see Understand auto-placement and affinity.
Dedicated Hosts provide comprehensive Bring Your Own License (BYOL) support, and that’s why they’re usually used. They allow you to use your existing per-socket, per-core, or per-VM software licenses, including Windows Server, SQL Server, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, or other software licenses that are bound to VMs, sockets, or physical cores, subject to your license terms.
You don’t pay for instances you launch on the host, instead you pay for the whole host:
-
On demand: hourly price for renting the whole host.
-
Reservations and Savings Plans: you can commit for 1/3 years and pay with:
-
Upfront
-
Partial Upfront
-
No Upfront
-
An host is designed to run a single instance type, while size can usually vary. For example, on a A1 host (1 socket, 16 cores) you can run:
-
16x A1.medium
-
8x A1.large
-
4x A1.xlarge
-
2x A1.2xlarge
-
1x A1.4xlarge
Some hosts require to declare in advance the size for ALL the instances. Nitro-based hosts don’t have this limittation. You can mix sizes.
RHEL, SUSE Linux and Windows, RDS are not supported. (?)
You can’t use Placement Groups.
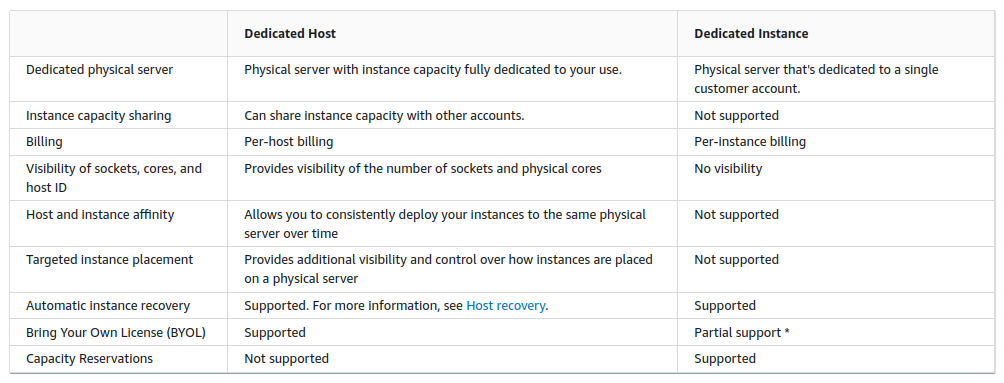
Dedicated hosts can be shared with accounts in the organization using the Resource Access Manager (RAM). The other accounts can only see instances they create while you can view but cannot control instances they create.
Dedicated Instances
Show slides

Dedicated Instances are physically isolated at the host hardware level from instances that belong to other AWS accounts, even if those accounts are linked to a single payer account.
You pay:
-
Hourly fee per used region
-
Hourly fee for instance usage
| Dedicated Instances might share hardware with other instances from the same AWS account that are not Dedicated Instances. |
-
Provide no visibility or control over instance placement.
-
Do not support host affinity.
-
If you stop and start a Dedicated Instance, it might not run on the same host.
-
You cannot target a specific host on which to launch or run an instance.
-
Provide limited support for Bring Your Own License (BYOL)
There are no performance, security, or physical differences between Dedicated Instances and instances on Dedicated Hosts.
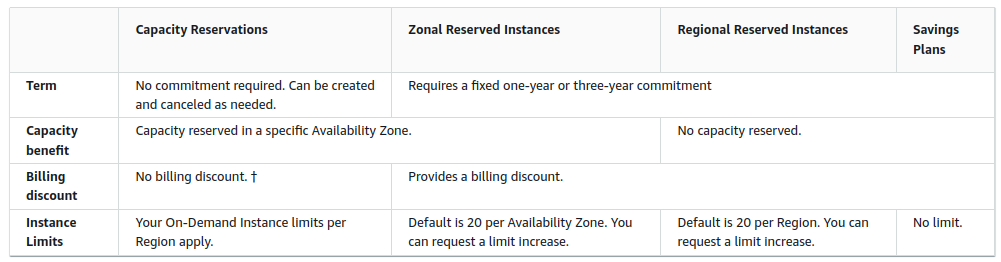
Capacity Reservations
Show slides

Concepts
You can create Capacity Reservations at any time, without entering into a one-year or three-year term commitment.
The capacity becomes available and billing starts as soon as the Capacity Reservation is provisioned in your account.
You can also use the billing discounts offered by Savings Plans and Regional Reserved Instances to reduce the cost of a Capacity Reservation.
Creating a capacity reservation
When you create a Capacity Reservation, you specify:
-
The Availability Zone in which to reserve the capacity
-
The number of instances for which to reserve capacity
-
The instance attributes, including the instance type, tenancy, and platform/OS
Types of Capacity Reservations
-
On-Demand Capacity Reservations
-
Capacity Blocks for ML (GPU instances)
Use cases (On-demand)
-
Scaling events – Create On-Demand Capacity Reservations ahead of your business-critical events to ensure that you can scale when you need to.
-
Regulatory requirements and disaster recovery – Use On-Demand Capacity Reservations to satisfy regulatory requirements for high availability, and reserve capacity in a different Availability Zone or Region for disaster recovery.
Use On-Demand Capacity Reservations if you have strict capacity requirements, and are running business-critical workloads that require capacity assurance. With On-Demand Capacity Reservations, you can ensure that you’ll always have access to the Amazon EC2 capacity you’ve reserved for as long as you need it.