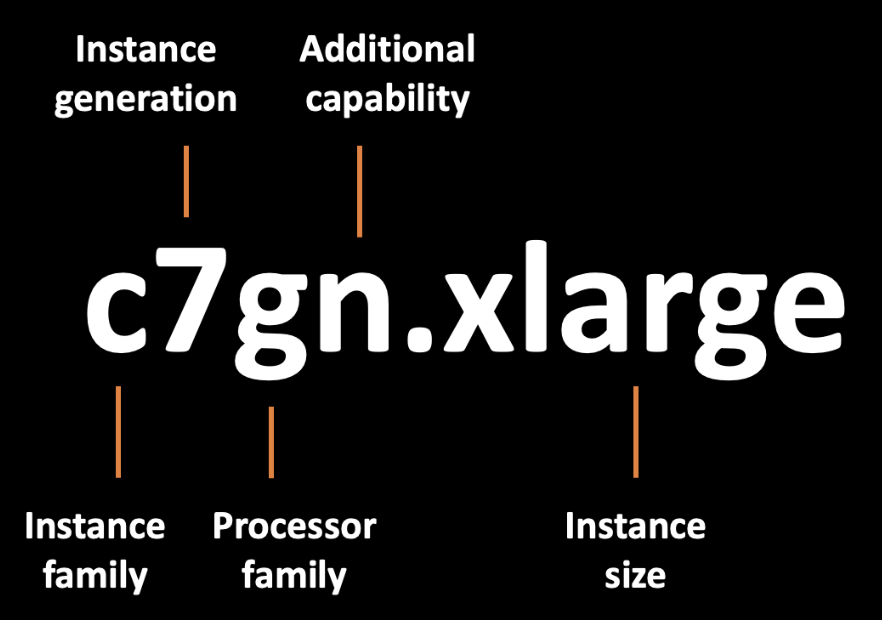
Instance Types
Show slides
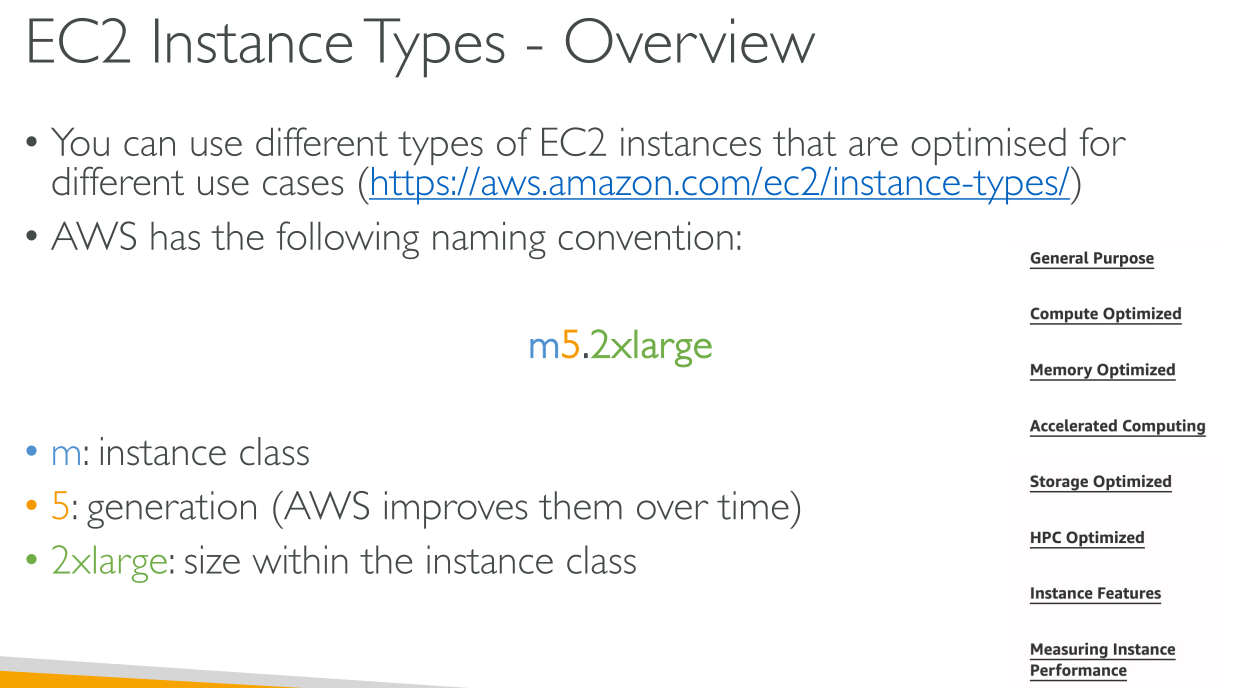

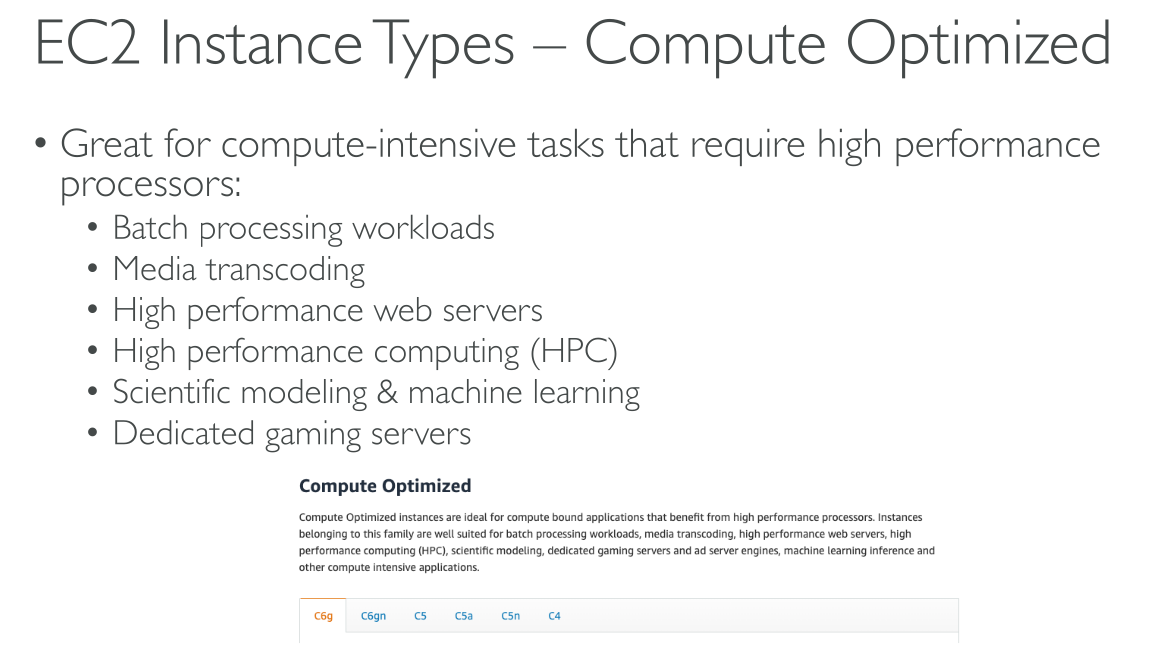
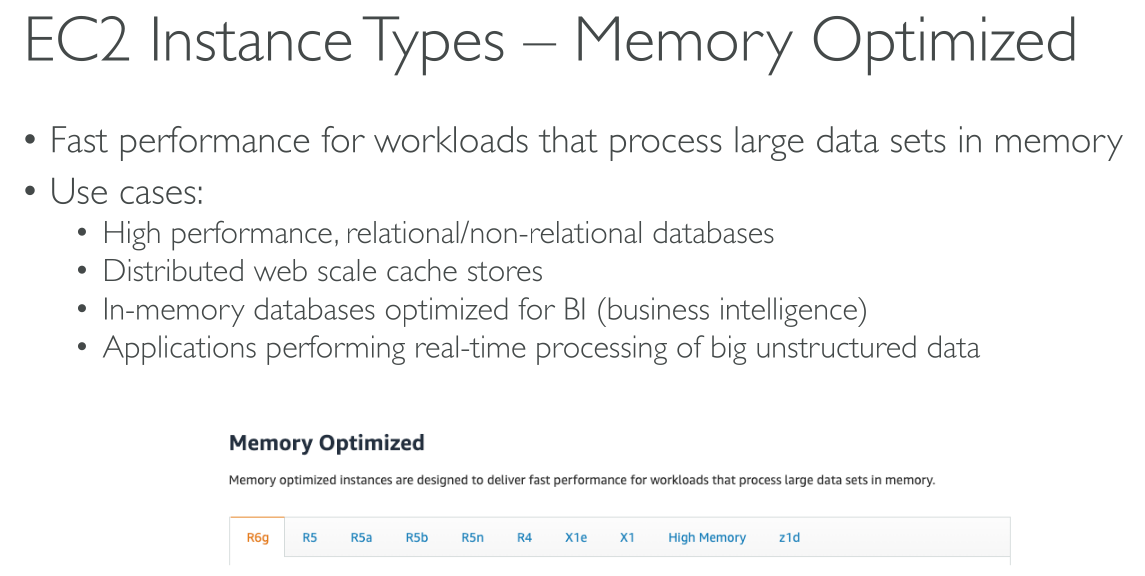
Amazon EC2 dedicates some resources of the host computer, such as CPU, memory, and instance storage, to a particular instance. Amazon EC2 shares other resources of the host computer, such as the network and the disk subsystem, among instances. If each instance on a host computer tries to use as much of one of these shared resources as possible, each receives an equal share of that resource. However, when a resource is underused, an instance can consume a higher share of that resource while it’s available.
Each instance type provides higher or lower minimum performance from a shared resource. For example, instance types with high I/O performance have a larger allocation of shared resources. Allocating a larger share of shared resources also reduces the variance of I/O performance.
Hardware specifications
Intel processor features:
-
Intel AES New Instructions (AES-NI): All current generation EC2 instances support this processor feature
-
Intel Advanced Vector Extensions (Intel AVX, Intel AVX2, and Intel AVX-512): These features are only available on instances launched with HVM AMIs
-
Intel Turbo Boost Technology
-
Intel Deep Learning Boost (Intel DL Boost): M5n, R5n, M5dn, M5zn, R5b, R5dn, D3, D3en, and C6i. C5 and C5d instances support VNNI for only 12xlarge, 24xlarge, and metal instances
Find an instance type
⇒ Generation and memory constraint
# Output all the current generation types that provide 4GiB of memory
$ aws ec2 describe-instance-types --filters "Name=current-generation,Values=true" "Name=memory-info.size-in-mib,Values=4096" --query "InstanceTypes[*].[InstanceType]" --output text | sort
# Output all the current generation types that provide 4GiB of memory describing VCpus and Memory configurations
$ aws ec2 describe-instance-types --filters "Name=current-generation,Values=true" "Name=memory-info.size-in-mib,Values=4096" --query "InstanceTypes[*].[InstanceType,VCpuInfo.DefaultVCpus,MemoryInfo.SizeInMiB]" --output json⇒ By zone and region
$ aws ec2 describe-instance-type-offerings --location-type "availability-zone" --filters Name=location,Values=us-east-2a --region us-east-2 --query "InstanceTypeOfferings[*].[InstanceType]" --output text | sortChanging the instance type
-
You must stop your Amazon EBS-backed instance before you can change its instance type
-
When you stop and start an instance, we move the instance to new hardware. If your instance has a public IPv4 address, we release the address and give your instance a new public IPv4 address. If you require a public IPv4 address that does not change, use an Elastic IP address
-
You can’t change the instance type of a Spot Instance
-
If your instance is in an Auto Scaling group, the Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling service marks the stopped instance as unhealthy, and may terminate it and launch a replacement instance. To prevent this, you can suspend the scaling processes for the group while you’re changing the instance type. See here.
-
When you change the instance type of an instance with NVMe instance store volumes, the updated instance might have additional instance store volumes, because all NVMe instance store volumes are available even if they are not specified in the AMI or instance block device mapping. Otherwise, the updated instance has the same number of instance store volumes that you specified when you launched the original instance
-
The maximum number of Amazon EBS volumes that you can attach to an instance depends on the instance type and instance size. You can’t change to an instance type or instance size that does not support the number of volumes that are already attached to your instance
Compatibility
Compatibility is determined in the following ways:
-
Virtualization type: paravirtual (PV) or hardware virtual machine (HVM).
-
Architecture
-
Network cards: You must select an instance type that supports the same number of network cards as the current instance type.
-
Enhanced networking: Instance types that support enhanced networking require the necessary drivers installed. To change from an instance type that does not support enhanced networking to an instance type that supports enhanced networking, you must install the ENA drivers or ixgbevf drivers on the instance
-
NVMe: If you change from an instance type that does not support NVMe to an instance type that supports NVMe, you must first install the NVMe drivers on your instance. Also, the device names for devices that you specify in the block device mapping are renamed using NVMe device names (/dev/nvme[0-26]n1). Therefore, to mount file systems at boot time using /etc/fstab, you must use UUID/Label instead of device names.
-
Volumes limits: The maximum number of Amazon EBS volumes that you can attach to an instance depends on the instance type and instance size.
Burstable performance instances
The EC2 burstable instances consist of T4g, T3a and T3 instance types, and the previous generation T2 instance types
Instance families
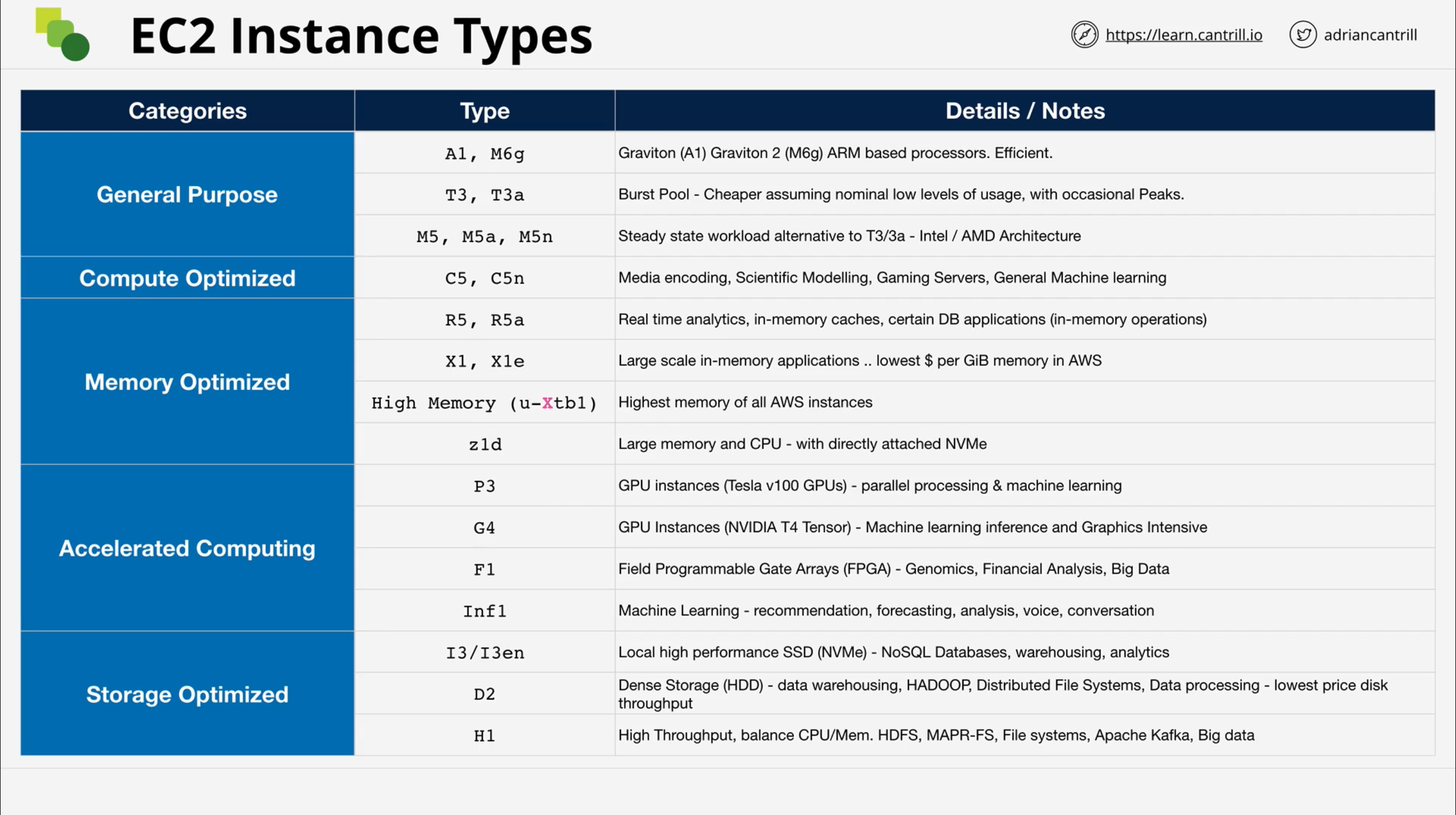
General purpose
Types: M5 | M5a | M5ad | M5d | M5dn | M5n | M5zn | M6a | M6g | M6gd | M6i | M6id | M6idn | M6in | M7a | M7g | M7gd | M7i | M7i-flex | Mac1 | Mac2 | Mac2-m2 | Mac2-m2pro | T2 | T3 | T3a | T4g
Compute optimized
Types: C5 | C5a | C5ad | C5d | C5n | C6a | C6g | C6gd | C6gn | C6i | C6id | C6in | C7a | C7g | C7gd | C7gn | C7i
Memory optimized
Types: R5 | R5a | R5ad | R5b | R5d | R5dn | R5n | R6a | R6g | R6gd | R6i | R6idn | R6in | R6id | R7a | R7g | R7gd | R7i | R7iz | U-3tb1 | U-6tb1 | U-9tb1 | U-12tb1 | U-18tb1 | U-24tb1 | X1 | X2gd | X2idn | X2iedn | X2iezn | X1e | z1d
Mac instances
Mac instances are available only as bare metal instances on Dedicated Hosts, with a minimum allocation period of 24 hours before you can release the Dedicated Host.
Mac instances are available only as On-Demand Instances. They are not available as Spot Instances or Reserved Instances. You can save money on Mac instances by purchasing a Savings Plan.