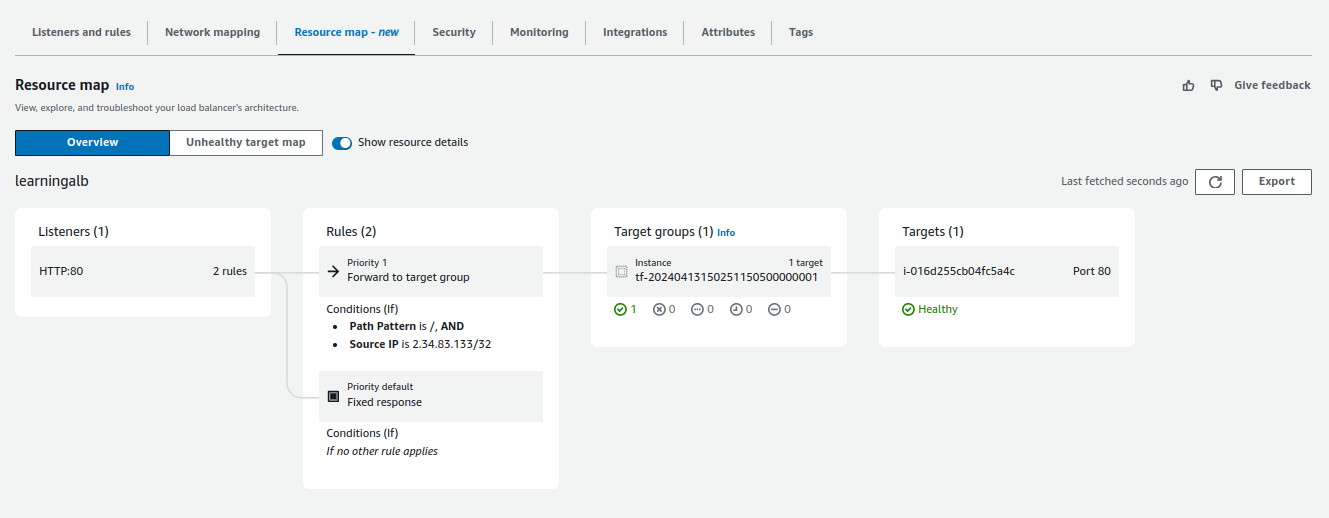
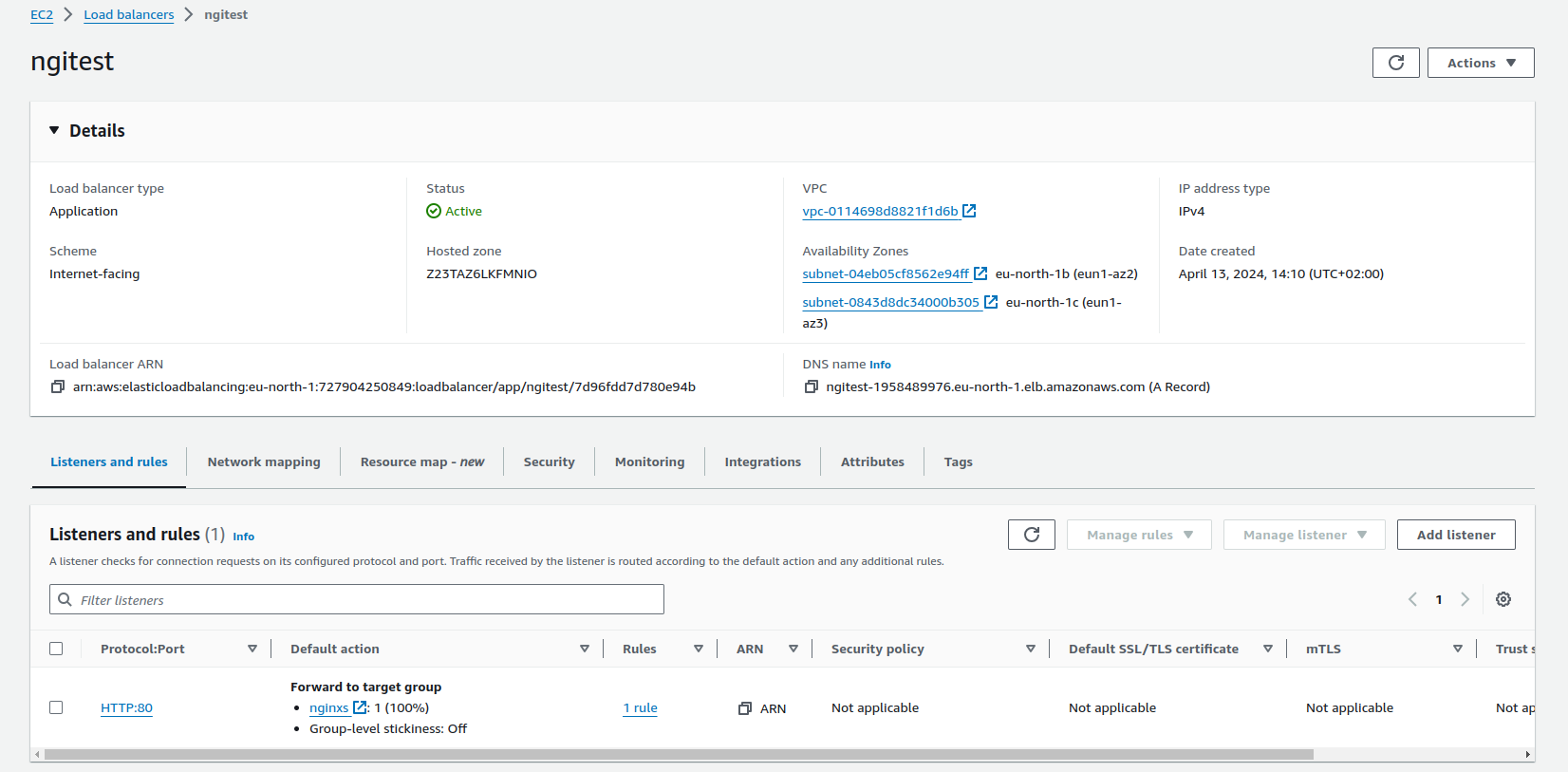
Application Load Balancer (ALB)
Show examples
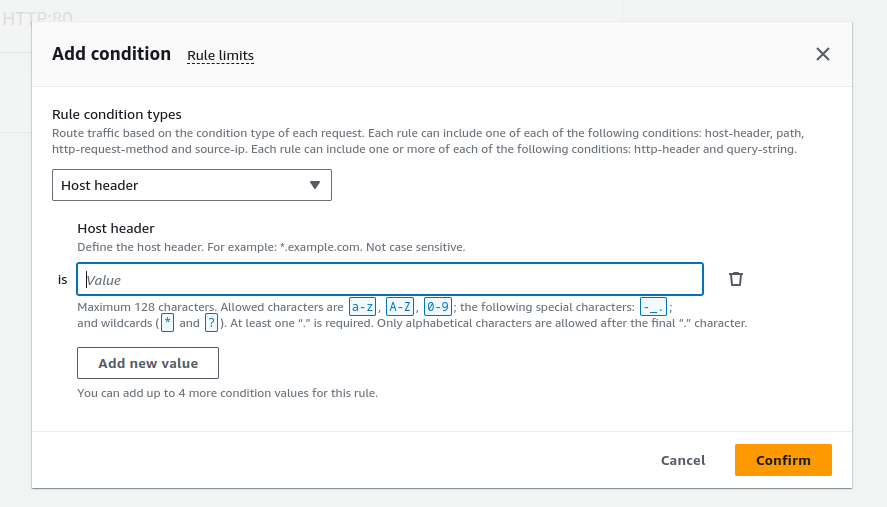
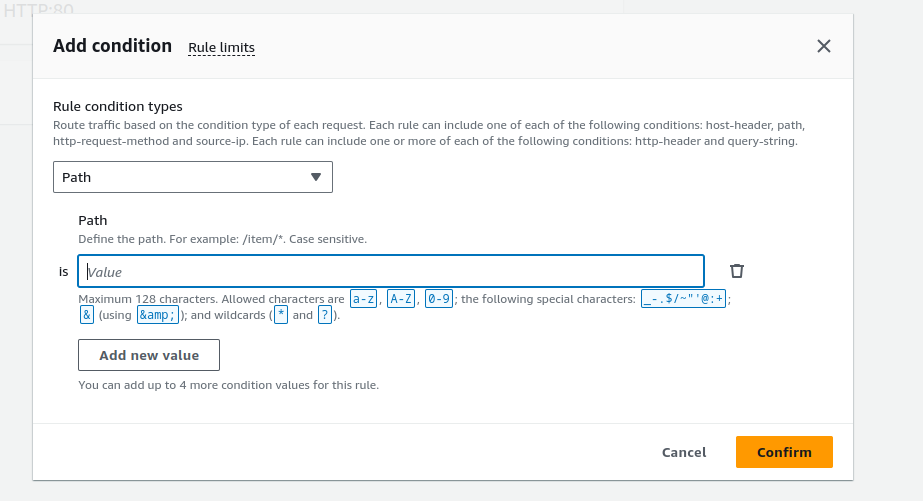
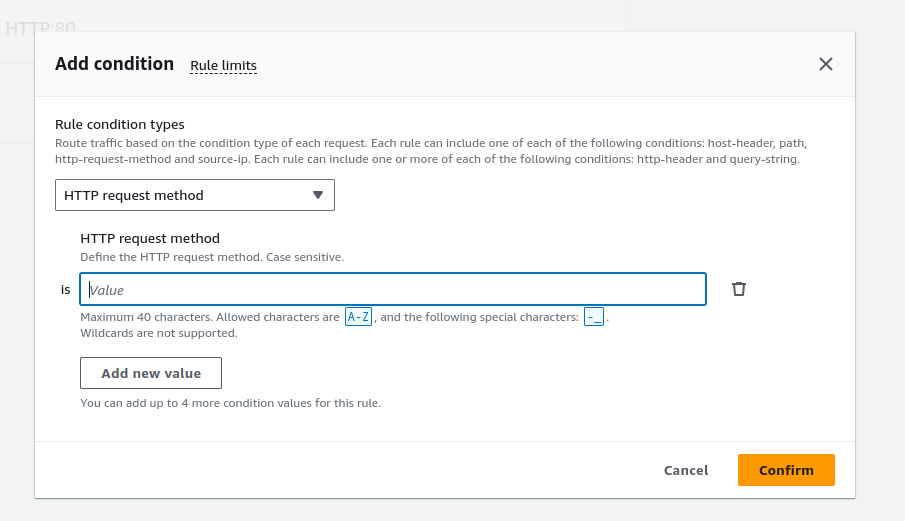
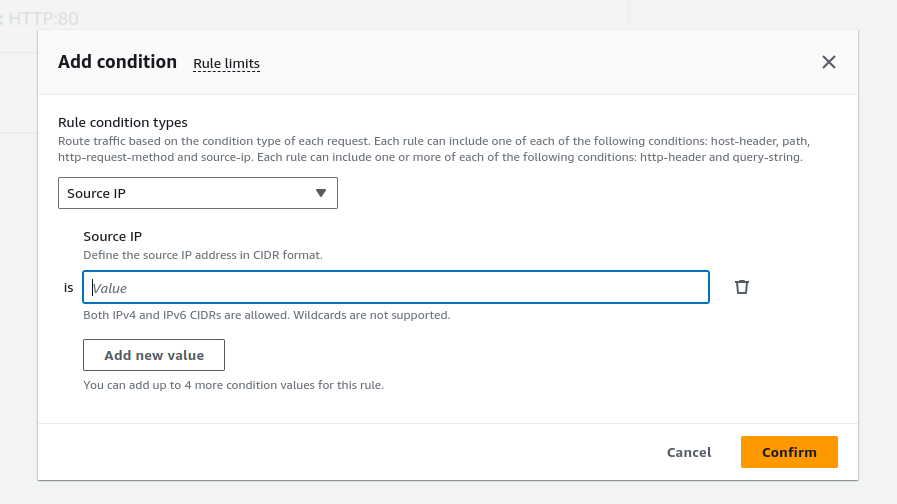
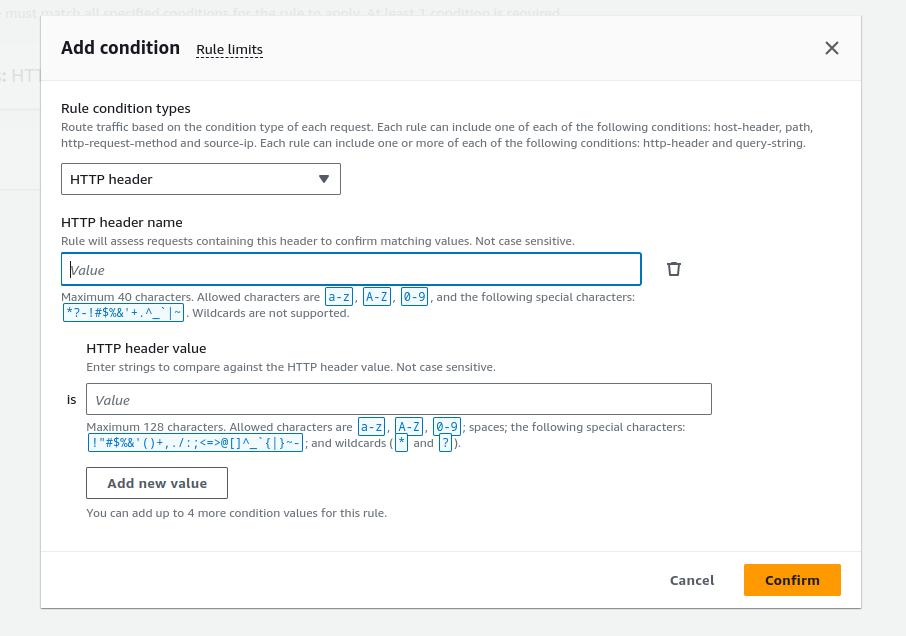
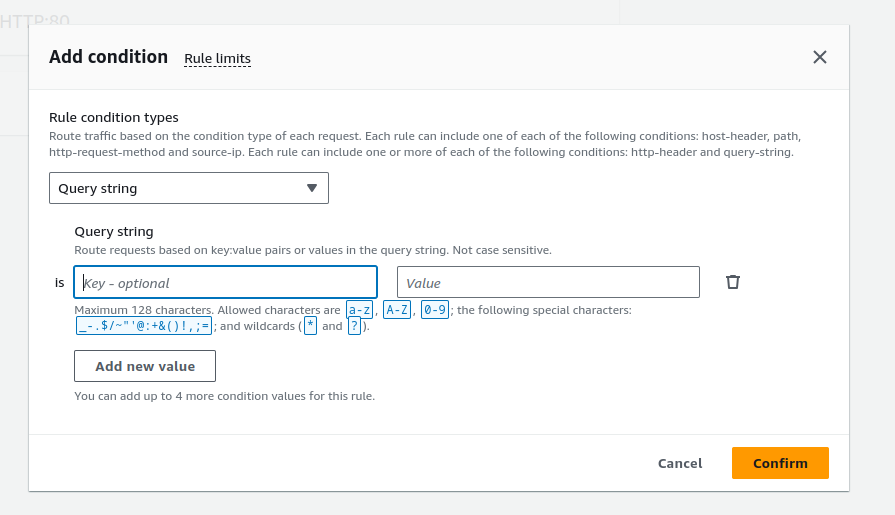
Supports:
-
HTTP/HTTPS (the load balancer ALWAYS terminates the TLS connection)
-
WebSocket (ws) and WebSocket Secure (wss)
Does NOT support:
-
Other Layer 7 protocols (like SSH, SMTP, …)
-
Layer 4 protocols (TCP, UDP, TLS)
Features
-
NO STATIC IP ADDRESS, DNS ONLY
-
Host conditions
-
Path conditions
-
Routing based on fields in the request: HTTP header conditions and methods, query parameters, and source IP addresses
-
Routing requests to multiple applications on a single EC2 instance: you can register an instance or IP address with multiple target groups, each on a different port.
-
Redirecting requests from one URL to another
-
Returning a custom HTTP response
-
Registering targets by IP address, including targets outside the VPC for the load balancer
-
Registering Lambda functions as targets
-
Authenticate users of your applications through their corporate or social identities before routing requests
-
containerized applications
-
monitoring the health of each service independently, as health checks are defined at the target group level and many CloudWatch metrics are reported at the target group level. Attaching a target group to an Auto Scaling group enables you to scale each service dynamically based on demand
-
Access logs contain additional information and are stored in compressed format
|
To ensure that your load balancer can scale properly, verify that each Availability Zone subnet for your load balancer has a CIDR block with at least a /27 bitmask (for example, 10.0.0.0/27) and at least eight free IP addresses per subnet |
Attributes
-
access_logs.s3.enabled
-
access_logs.s3.bucket
-
access_logs.s3.prefix
-
client_keep_alive.seconds
-
deletion_protection.enabled
-
idle_timeout.timeout_seconds
-
ipv6.deny_all_igw_traffic
-
routing.http.desync_mitigation_mode
-
routing.http.drop_invalid_header_fields.enabled
-
routing.http.preserve_host_header.enabled
-
routing.http.x_amzn_tls_version_and_cipher_suite.enabled
-
routing.http.xff_client_port.enabled
-
routing.http.xff_header_processing.mode: enables you to modify, preserve, or remove the X-Forward-For header in the HTTP request before the Application Load Balancer sends the request to the target. The possible values are append, preserve, and remove. The default is append. If the value is append, the Application Load Balancer adds the client IP address (of the last hop) to the X-Forward-For header in the HTTP request before it sends it to targets. If the value is preserve, the Application Load Balancer preserves the X-Forward-For header in the HTTP request, and sends it to targets without any change. If the value is remove, the Application Load Balancer removes the X-Forward-For header in the HTTP request before it sends it to targets.
-
routing.http2.enabled
-
waf.fail_open.enabled
WebSocket
Application Load Balancers provide native support for WebSockets. You can upgrade an existing HTTP/1.1 connection into a WebSocket (ws or wss) connection by using an HTTP connection upgrade. When you upgrade, the TCP connection used for requests (to the load balancer as well as to the target) becomes a persistent WebSocket connection between the client and the target through the load balancer.
You can use WebSockets with both HTTP and HTTPS listeners.
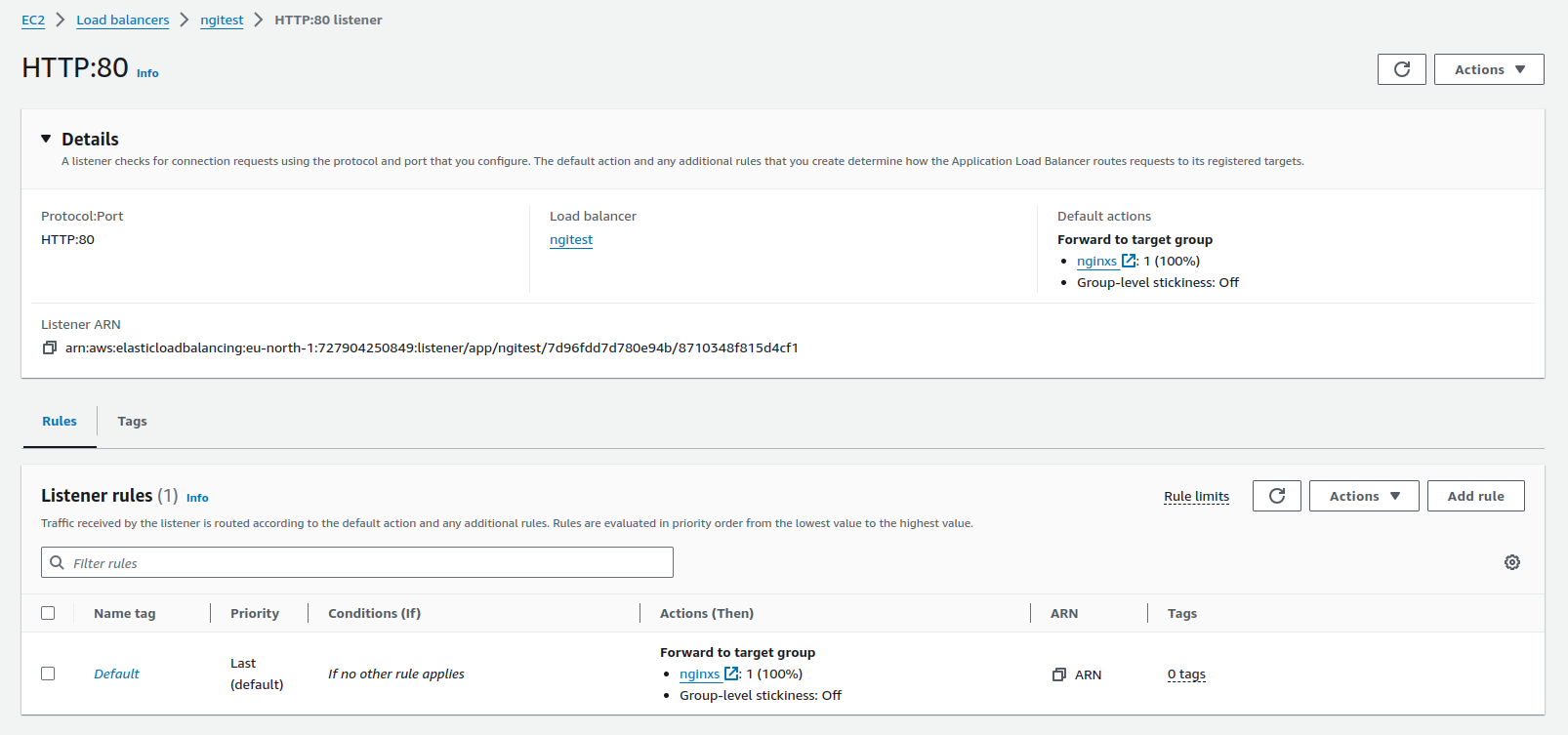
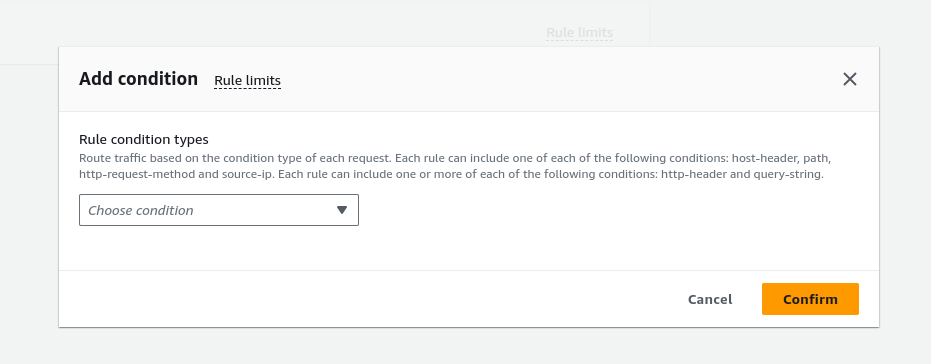
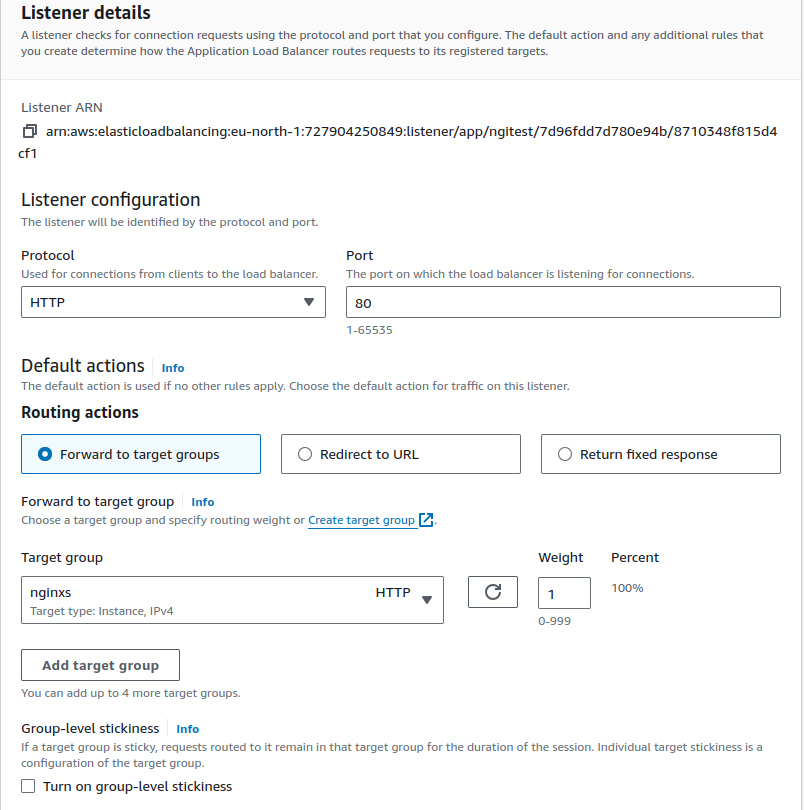
Rules
Each rule has a priority. Rules are evaluated in priority order, from the lowest value to the highest value. The default rule is evaluated last.
Action types
-
authenticate-cognito
-
authenticate-oidc
-
fixed-response
-
forward
-
redirect
Each rule must include exactly one of the following actions: forward, redirect, or fixed-response, and it must be the last action to be performed.
If the protocol version is gRPC or HTTP/2, the only supported actions are forward actions.
Routing Algorithms
-
round robin (default): routes requests evenly across healthy targets in the target group, in a sequential order.
-
Least outstanding requests: routes requests to the targets with the lowest number of in progress requests.
-
Weighted random: routes requests evenly across healthy targets in the target group, in a random order.
Automatic Target Weights (ATW) constantly monitors the targets running your applications, detecting significant performance deviations, known as anomalies. ATW provides the ability to dynamically adjust the amount of traffic routed to targets, through real time data anomaly detection.
Deregistration delay
Elastic Load Balancing stops sending requests to targets that are deregistering. By default, Elastic Load Balancing waits 300 seconds before completing the deregistration process, which can help in-flight requests to the target to complete. To change the amount of time that Elastic Load Balancing waits, update the deregistration delay value.
Slow start mode
By default, a target starts to receive its full share of requests as soon as it is registered with a target group and passes an initial health check. Using slow start mode gives targets time to warm up before the load balancer sends them a full share of requests.
Target Groups
Stickiness can be configured at this level.
You cannot register the IP addresses of another Application Load Balancer in the same VPC. If the other Application Load Balancer is in a VPC that is peered to the load balancer VPC, you can register its IP addresses.
You cannot register instances by instance ID if they are in a VPC that is peered to the load balancer VPC (same Region or different Region). You can register these instances by IP address.
Health Checks
-
Protocols: HTTP/HTTPS
-
Port
-
Path
-
Timeout
-
Interval
-
Healthy threshold
-
Unhealthy threshold
-
Matcher: the HTTP status code to expect from a successful response. It can be 200-499 (HTTP) or 0-99 (gRPC), multiple values or a range can be specified.
Target Groups attributes
-
deregistration_delay.timeout_seconds
-
load_balancing.algorithm.type
-
load_balancing.algorithm.anomaly_mitigation
-
load_balancing.cross_zone.enabled
-
slow_start.duration_seconds
-
stickiness.enabled
-
stickiness.app_cookie.cookie_name
-
stickiness.app_cookie.duration_seconds
-
stickiness.lb_cookie.duration_seconds
-
stickiness.type
-
target_group_health.dns_failover.minimum_healthy_targets.count
-
target_group_health.dns_failover.minimum_healthy_targets.percentage
-
target_group_health.unhealthy_state_routing.minimum_healthy_targets.count
-
target_group_health.unhealthy_state_routing.minimum_healthy_targets.percentage
The following target group attribute is supported if the target group type is lambda:
-
lambda.multi_value_headers.enabled