AWS Backup
AWS Backup is a fully-managed service that makes it easy to centralize and automate data protection across AWS services, in the cloud, and on premises. It lets you consolidate the backup/restore management and more in one place.
It can work cross-account and cross-region.
It offers:
-
PITR (Point-In-Time-Recovery) for supported services
-
On-Demand and scheduled backups
-
Centralized backup management
-
Policy-based backup using Backup Plans that define what and when to back up.
-
Tag-based backup: you don’t have to manually add resources to Backup Plans, you can use tags.
-
Lifecycle Management Policies help you save money moving data between storage classes.
-
Cross-Region backup
-
Cross-account management and cross-account backup using AWS Organizations
-
Auditing and reporting (with AWS Backup Audit Manager)
-
Incremental backups
-
Full AWS Backup management for some resources:
-
Independent encryption: AWS Backup automatically encrypts your backups with the KMS key of your AWS Backup vault, instead of using the same encryption key as your source resource.
-
awsbackup Amazon Resource Names (ARNs): Backup ARNs begin with
arn:aws:backupinstead of 'arn:aws:source-resource'. This allows you to create access policies that apply specifically to backups and not the source resources. -
Centralized backup billing and Cost Explorer cost allocation tags
-
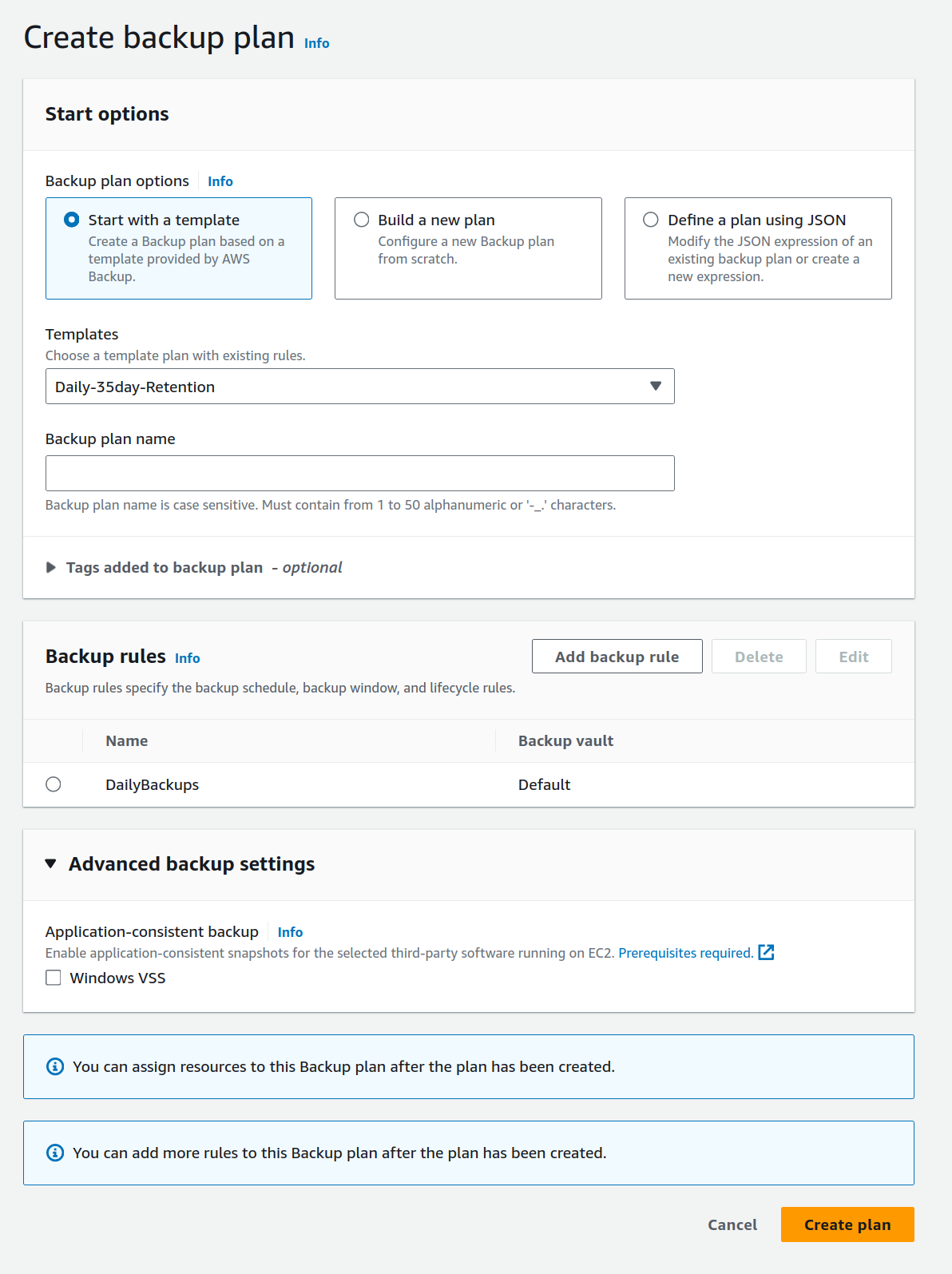
Backup Plans
A backup plan is a policy expression that defines when and how you want to back up your AWS resources. You can assign resources to backup plans, and AWS Backup automatically backs up and retains backups for those resources according to the backup plan.
By default, backup windows are optimized by AWS Backup. You can customize the backup window in the console or programmatically.
When creating the backup plan you assign AWS resources to its scope.
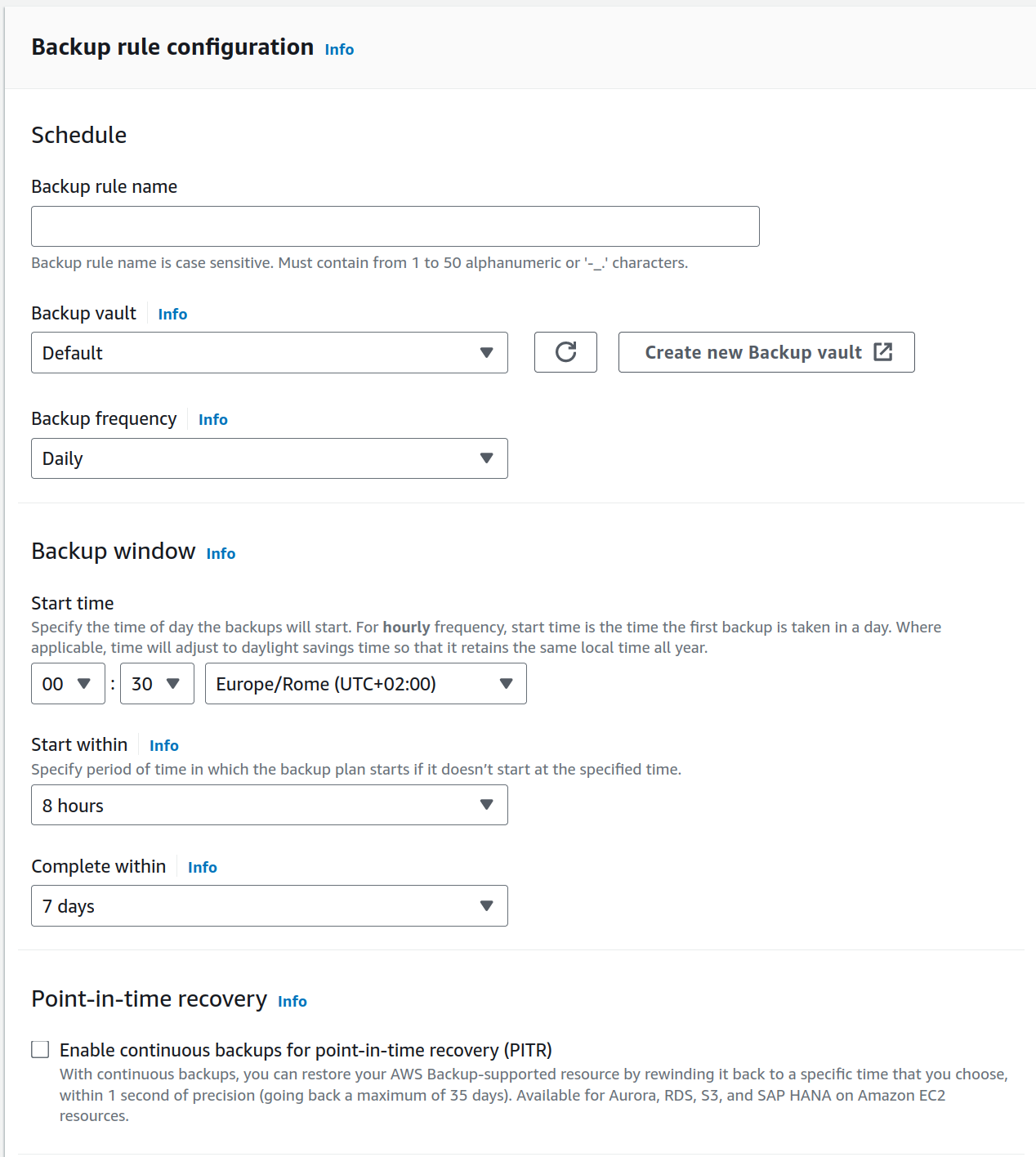
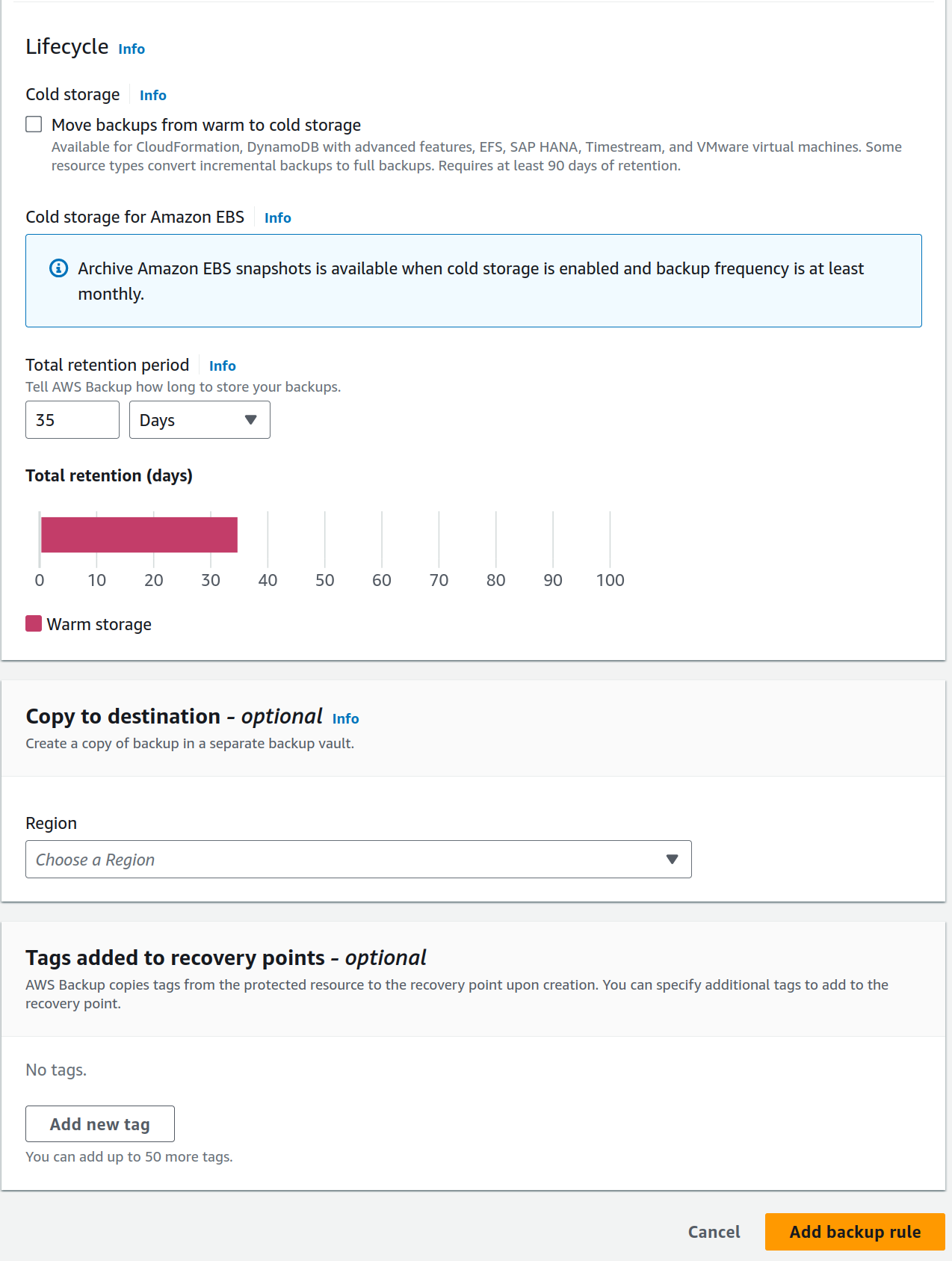
You can specify: * Frequenct * Backup Window * Transition to cold storage * Retention period
Resources (targets)
Here’s a list of supported resources:
-
Storage:
-
Amazon FSx file systems
-
Amazon S3 data
-
Amazon EFS
-
Amazon EBS
-
AWS Storage Gateway
-
-
Compute:
-
Amazon EC2
-
VMware virtual machines
-
-
Databases:
-
Amazon RDS and Aurora
-
Amazon DocumentDB
-
Amazon DynamoDB
-
Amazon Neptune
-
Amazon Timestream
-
AWS BackInt, AWS Systems Manager for SAP, and SAP HANA
-
-
Others
-
AWS BackInt
-
AWS Organizations
-
AWS CloudFormation
-
Vaults (destinations)
AWS Backup further secures your backups in backup vaults, which separates them safely from their source instances. For example, your vault will retain your Amazon EC2 and Amazon EBS backups according to the lifecycle policy you choose, even if you delete the source Amazon EC2 instance and Amazon EBS volumes.
Backup vaults offer encryption and resource-based access policies.