ElastiCache for Redis
Deployment options
Serverless
-
Cluster mode only.
-
There’s a single endpoint for incoming connections.
-
Multi-AZ is by design. Data is replicated asynchronously (!).
-
Encryption at rest is always enabled.
-
Encryption in transit is always enabled.
-
Automatic and manual backups with no performance impact.
-
No support for Global Data Store.
-
No support for Data Tiering.
Benefits:
-
No capacity planning
-
Pay-per-use
-
High-availability: ElastiCache Serverless automatically replicates your data across multiple Availability Zones (AZ) for high-availability. It automatically monitors the underlying cache nodes and replaces them in case of failures. It offers a 99.99% availability SLA for every cache.
-
Automatic software upgrades: ElastiCache Serverless automatically upgrades your cache to the latest minor and patch software version without any availability impact to your application. When a new Redis major version is available, ElastiCache will send you a notification.
-
Security: Serverless always encrypts data in transit and at rest. You can use a service managed key or use your own Customer Managed Key to encrypt data at rest.
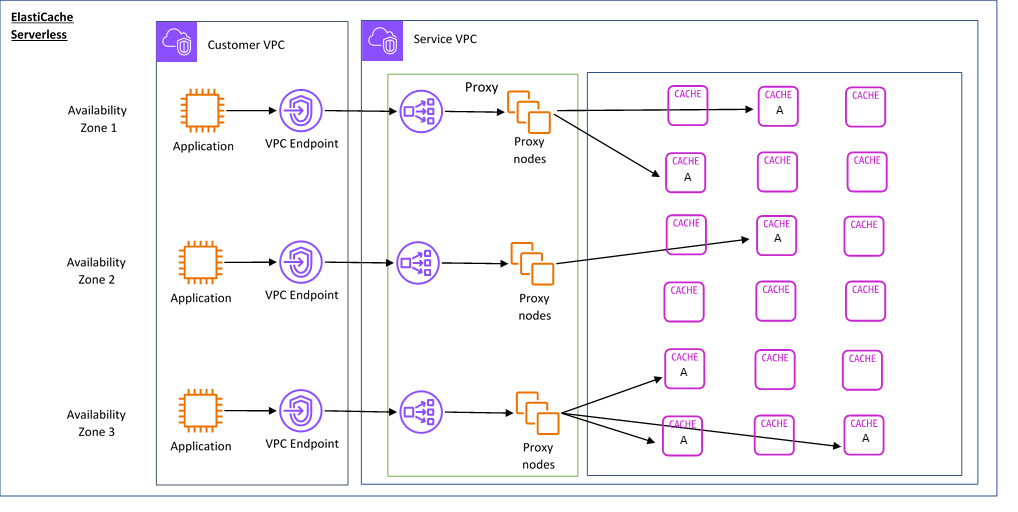
ElastiCache creates a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Endpoint in the subnets of your choice in your VPC. Your application can connect to the cache through these VPC Endpoints.
Self-designed
-
You can enable or disable cluster mode.
-
Clients connect to each individual node, in case of failure they need to discover new nodes.
-
You can enable Multi-AZ. Data is replicated asynchronously (!).
-
You can enable Encryption at rest.
-
You can enable Encryption in transit.
-
Automatic and manual backups with performance impact depends on reserved memory.
-
Global Data Store: Single region writes, multi-region reads.
-
Data Tiering: supported. RAM + Local SSD
Components:
-
Nodes: A node is a fixed-size chunk of secure, network-attached RAM. Each cache node has its own Domain Name Service (DNS) name and port.
-
Shards (node group): A group of 1-6 nodes (only available in cluster mode obviously). 1 shard only with cluster mode disabled.
Benefits:
-
Design your own cluster: With ElastiCache, you can design your own cluster and choose where you want to place your cache nodes. For example, if you have an application that wants to trade-off high-availability for low latency, you can choose to deploy your cache nodes in a single AZ. Alternatively, you can design your cluster with nodes across multiple AZs to achieve high-availability.
-
Fine-grained control: When designing our own cluster, you have more control over fine-tuning the settings on your cache. For example, you can use Redis-specific parameters to configure the cache engine.
-
Scale vertically and horizontally: You can choose to manually scale your cluster by increasing or decreasing the cache node size when needed. You can also scale horizontally by adding new shards or adding more replicas to your shards. You can also use the Auto-Scaling feature to configure scaling based on a schedule or scaling based on metrics like CPU and Memory usage on the cache.
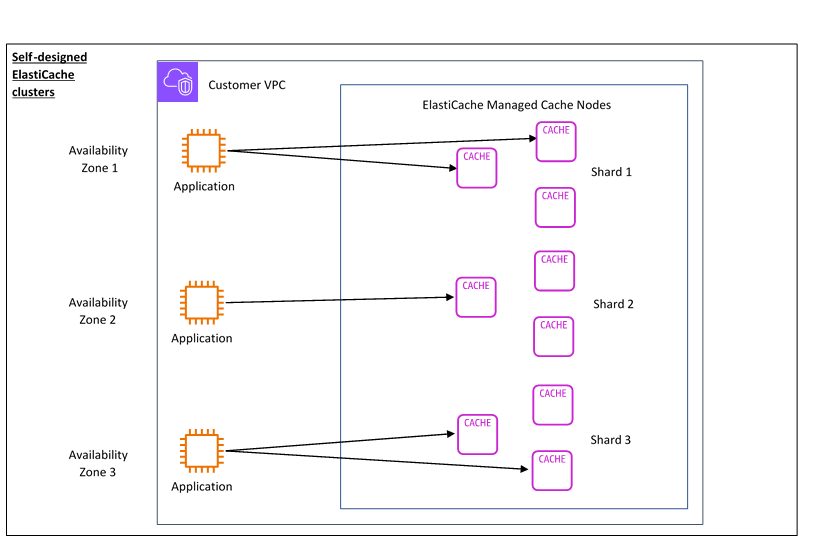
Features
-
Data-tiering: More frequently accessed data is stored in memory and less frequently accessed data is stored on disk (SSD).
-
Replication: Replication is implemented by grouping from two to six nodes in a shard (in the API and CLI, called a node group). One of these nodes is the read/write primary node. All the other nodes are read-only replica nodes. Each replica node maintains a copy of the data from the primary node. Replica nodes use asynchronous replication mechanisms to keep synchronized with the primary node. When cluster mode is disabled replication can be active: the shard will consist of 1-2-6 nodes.
-
Endpoints:
-
Single-node endpoints (Cluster mode disabled): used to connect to a single node both read and write.
-
Multi-node endpoints (Cluster mode disabled):
-
Primary endpoint: connects to the primary node Read/Write. Updated in case of failover.
-
Reader endpoint: evenly splits connections among read replicas.
-
-
Redis endpoints (Cluster mode enable): it’s a single endpoint to handle read and write transparently.
-
-
Auto-scaling: To use automatic scaling, you define and apply a scaling policy that uses CloudWatch predefined metrics and target values with a default cooldown period of 900s (scale in) and 600s (scale out). ElastiCache for Redis supports scaling for Shards and Replicas using Target tracking scaling policies or Scheduled scaling.
| Custom metrics are not available for selection using the AWS Management Console. Alternatively, you can use either the AWS CLI or the Application Auto Scaling API to apply a scaling policy based on a predefined or custom metric. |
Backups
A backup is a point-in-time copy of a Redis cache. ElastiCache enables you to take a backup of your data at any time or setup automatic backups. Backups can be used to restore an existing cache or to seed a new cache. Backups consist of all the data in a cache plus some metadata. Amazon ElastiCache caches running Redis can back up their data by creating a snapshot. You can use the backup to restore a cache or seed data to a new cache.
Limitations:
-
Backup and restore are supported only for caches running on Redis.
-
* During any contiguous 24-hour period, you can create no more than 20 manual backups per node in the cluster.
-
When cluster mode is enabled Redis only supports taking backups on the cluster level.
-
During the backup process, you can’t run any other API or CLI operations on the cluster.
-
If using clusters with data tiering, you cannot export a backup to Amazon S3.
For automated backups you need to specify a Backup start time and a Backup retention limit (max 35 days). Backups are retained in S3.
It’s also possible to export backups on S3.
Global Datastores
Creates cross-Region read replica clusters for ElastiCache for Redis to enable low-latency reads and disaster recovery across AWS Regions.
-
Primary (active) cluster: accepts writes that are replicated to all clusters within the global datastore. A primary cluster also accepts read requests.
-
Secondary (passive) cluster: only accepts read requests and replicates data updates from a primary cluster. A secondary cluster needs to be in a different AWS Region.
Use cases
Read How to take advantage of Redis just adding it to your stack from Salvatore Sanfilippo.
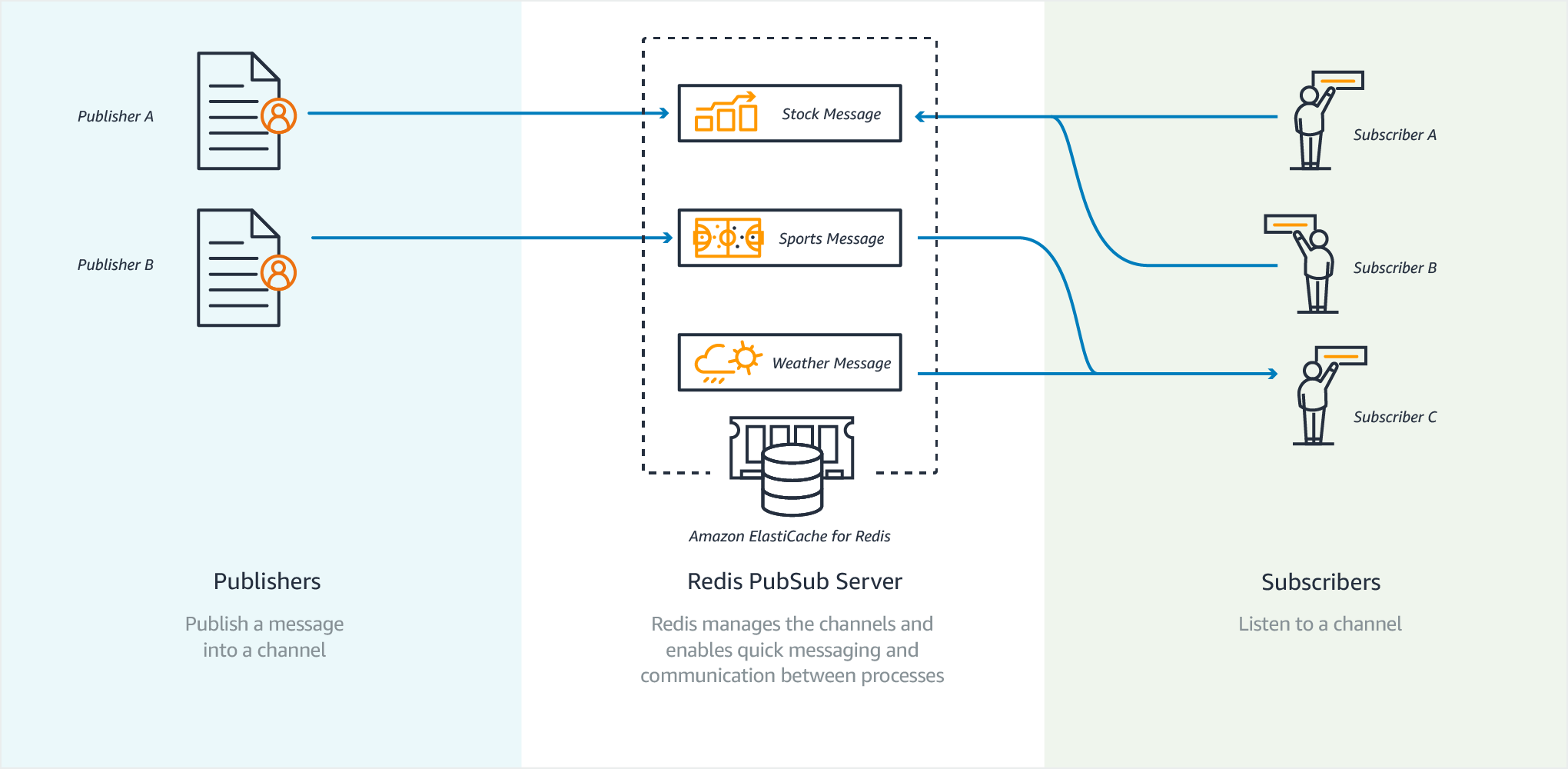
In-Memory Data Store
How to decide what data to cache:
-
Speed and expense – If the interesting data requires a slow and expensive query to get, it’s a candidate for caching.
-
Data and access pattern – It doesn’t make sense to cache data that changes quickly or is seldom accessed. For caching to provide a real benefit, the data should be relatively static and frequently accessed.
-
Staleness – By definition, cached data is stale data. Even if in certain circumstances it isn’t stale, it should always be considered and treated as stale. To tell whether your data is a candidate for caching, determine your application’s tolerance for stale data.
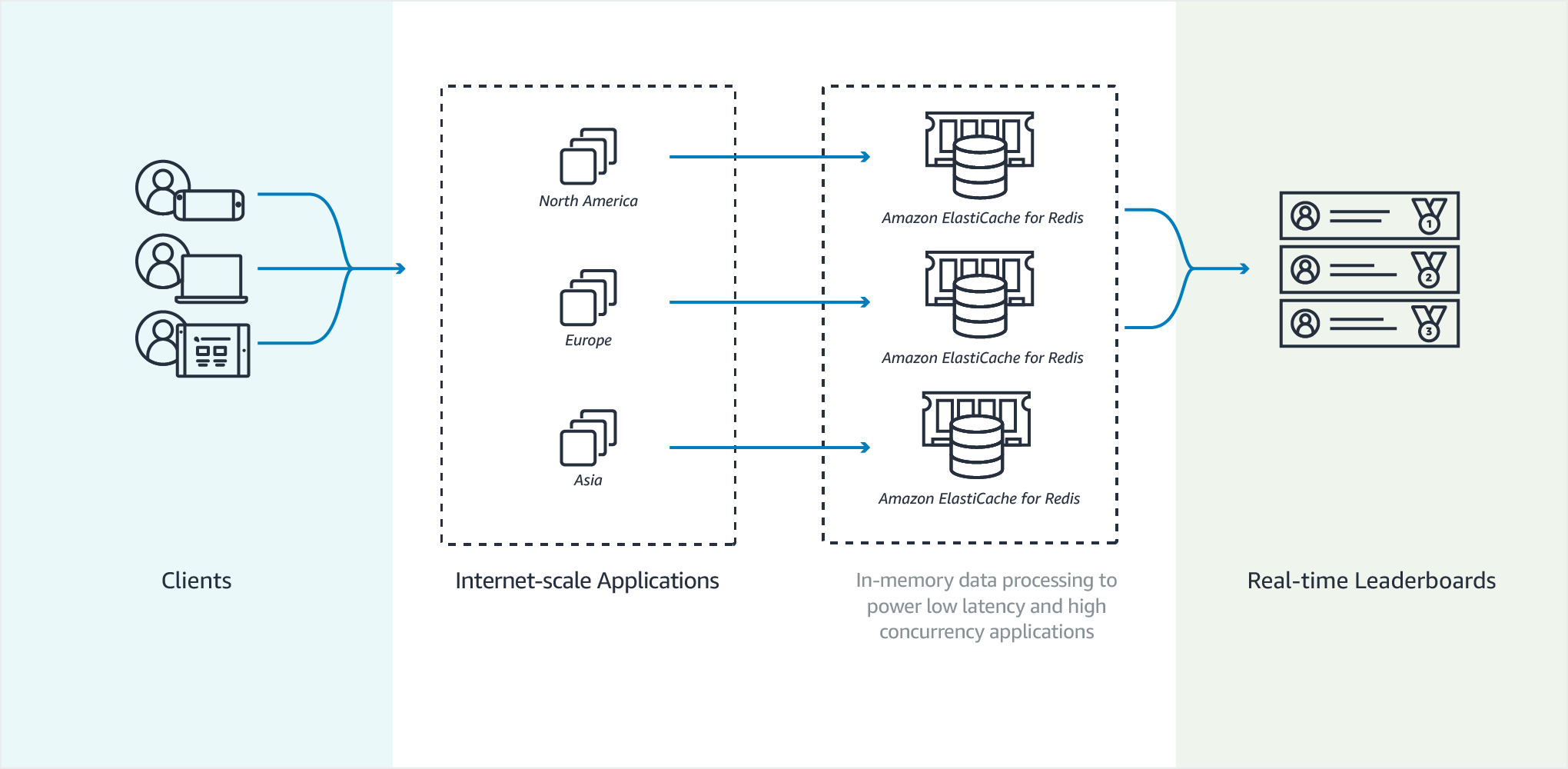
Gaming Leaderboards (Redis Sorted Sets)
Leaderboards, such as the top 10 scores for a game, are computationally complex. This is especially true when there is a large number of concurrent players and continually changing scores. Redis sorted sets guarantee both uniqueness and element ordering.