Amazon Redshift
Redshift is a provisioned and serverless (two versions) Petabyte-scale Data Warehouse. A data warehouse is where many different databases can push data for long-term REPORTING and ANALYTICS purposes, NOT for OPERATIONAL-style usage.
Redshift is an OLAP database that uses a parallel query engine. It’s based on PostgreSQL, but it’s not used for OLTP.
It can be used for single analysis: load your data, perform the analysis and destroy it. Redshift Spectrum is particularily useful for this scenario because it doesn’t require you to load data upfront, you just need to export it on S3.
You can’t use Redshift like you use Athena for ad-hoc queries, it has to be provisioned and data must be loaded first. Apart from that it has much faster queries, joins and aggregations compared to Athena, this is because, differently from Athena, Redshift has indexes.
Integrations
Redshift integrates with other AWS services, like Quicksight or Tableau.
It has a SQL-like interface and can be connected to using JDBC/ODBC connections.
Architecture (Provisioned)
Amazon Redshift clusters run in Amazon EC2 instances that are configured for the Amazon Redshift node type and size that you select.
It’s a mostly Single-AZ service, but Multi-AZ mode is available for some cluster types (useful for DR). If you can’t use Multi-AZ you can use Snapshots for DR.
Redshift runs in a cluster with a leader and compute nodes. The leader node receives queries from client applications, parses the queries, and develops query execution plans. The leader node then coordinates the parallel execution of these plans with the compute nodes and aggregates the intermediate results from these nodes. It then finally returns the results back to the client applications.
Enhanced VPC Routing
When you use Amazon Redshift enhanced VPC routing, Amazon Redshift forces all COPY and UNLOAD traffic between your cluster and your data repositories through your virtual private cloud (VPC) based on the Amazon VPC service.
You can use standard VPC features, such as VPC security groups, network access control lists (ACLs), VPC endpoints, VPC endpoint policies, internet gateways, and Domain Name System (DNS) servers. Which means that COPY from S3 can happen privately.
Snapshots
These are Point-in-time incremental backups of a cluster stored in S3.
You can restore a new cluster from a snapshot. Also, you can configure Redshift to automatically copy snapshot to another region for DR.
Ingestion
Avoid small inserts to optimize performance.
COPY Command
The COPY command leverages the Amazon Redshift massively parallel processing (MPP) architecture to read and load data in parallel from:
-
files on Amazon S3
-
DynamoDB table
-
from text output (of a command) from one or more remote hosts: COPY connects to the remote hosts using SSH and runs commands on the remote hosts to generate text output.
To load data from another AWS resource, your cluster must have permission to access the resource and perform the necessary actions.
copy customer from 's3://mybucket/prefix'
iam_role 'arn:aws:iam::12345678901:role/MyRedshiftRole';Federated Queries
Like in Athena, you can directly query data stored in remote data sources. Like Postgres or MySQL in RDS/Aurora.
CREATE EXTERNAL SCHEMA apg
FROM POSTGRES
DATABASE 'database-1' SCHEMA 'myschema'
URI '<endpoint to aurora hostname>'
IAM_ROLE 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/Redshift-SecretsManager-RO'
SECRET_ARN 'arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-west-2:123456789012:secret:federation/test/dataplane-apg-creds-YbVKQw';Redshift Spectrum
Redshift Spectrum allows to efficiently query and retrieve structured and semistructured data from files in Amazon S3 without having to load the data into Amazon Redshift tables.
Amazon Redshift Spectrum resides on dedicated Amazon Redshift servers that are independent of your cluster. Amazon Redshift pushes many compute-intensive tasks, such as predicate filtering and aggregation, down to the Redshift Spectrum layer. Thus, Redshift Spectrum queries use much less of your cluster’s processing capacity than other queries. Redshift Spectrum also scales intelligently. Based on the demands of your queries, Redshift Spectrum can potentially use thousands of instances to take advantage of massively parallel processing.
You create Redshift Spectrum tables by defining the structure for your files and registering them as tables in an external data catalog (AWS Glue, Athena, self-managed HIVE Metastore).
Optionally, you can partition the external tables on one or more columns to improve performance.
Redshift Architectures
Rich Data Platform Architecture
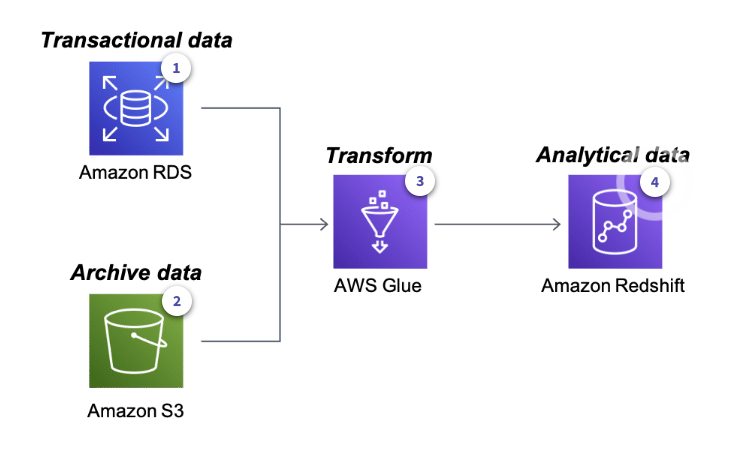
-
RDS contains current operational data
-
S3 contains archived data
-
Glue can source from both RDS and S3 to load data in Redshift
-
Redshift allows for storing and querying data
Event-drive Data Analysis Architecture
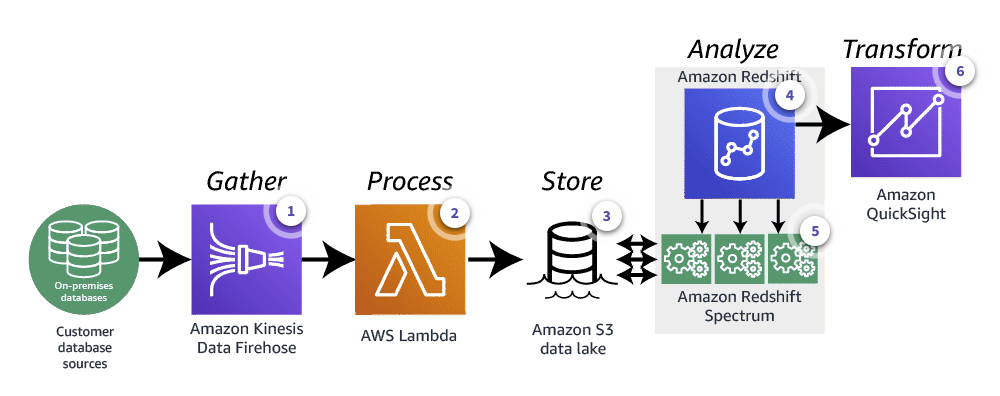
-
Amazon Data Firehose gathers data from on-prem databases
-
A Lambda function loads data into a S3 Data Lake
-
S3 is the Data Lake
-
Redshift already contains analytical data
-
Redshift Spectrum queries both the data present in the Redshift tables and the S3 Data Lake (without loading data to Redshift)
-
QuickSight is used to visualize data